
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Diggers in the Earth, by Eva March Tappan This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net Title: Diggers in the Earth Author: Eva March Tappan Release Date: March 6, 2008 [EBook #24762] Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK DIGGERS IN THE EARTH *** Produced by Diane Monico and The Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images generously made available by The Internet Archive/American Libraries.)
Author of "England's Story," "American Hero Stories,"
"Old World Hero Stories," "Story of the Greek People,"
"Story of the Roman People," etc. Editor of
"The Children's Hour."

THE INDUSTRIAL READERS
By Eva March Tappan
| I. | THE FARMER AND HIS FRIENDS. 50 cents. |
| II. | DIGGERS IN THE EARTH. 50 cents. |
| III. | MAKERS OF MANY THINGS. 50 cents. |
| IV. | TRAVELERS AND TRAVELING. 50 cents. |
The foregoing are list prices, postpaid
COPYRIGHT, 1916, BY EVA MARCH TAPPAN
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
First printing April 1916;
Reprinted December 1916
The Riverside Press
CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS
U. S. A.
The four books of this series have been written not merely to provide agreeable reading matter for children, but to give them information. When a child can look at a steel pen not simply as an article furnished by the city for his use, but rather as the result of many interesting processes, he has made a distinct growth in intelligence. When he has begun to apprehend the fruitfulness of the earth, both above ground and below, and the best way in which its products may be utilized and carried to the places where they are needed, he has not only acquired a knowledge of many kinds of industrial life which may help him to choose his life-work wisely from among them; but he has learned the dependence of one person upon other persons, of one part of the world upon other parts, and the necessity of peaceful intercourse. Best of all, he has learned to see. Wordsworth's familiar lines say of a man whose eyes had not been opened,—
These books are planned to show the children that there is "something more"; to broaden their horizon; to reveal to them what invention has accomplished and what wide room for invention still remains; to teach them that reward comes to the[Pg iv] man who improves his output beyond the task of the moment; and that success is waiting not for him who works because he must, but him who works because he may.
Acknowledgment is due to the Lehigh Valley Railroad, Jones Brothers Company, Alpha Portland Cement Company, Dwight W. Woodbridge, the Utah Copper Company, the Aluminum Company of America, the Diamond Crystal Salt Company, T. W. Rickard, and others, whose advice and criticism have been of most valuable aid in the preparation of this volume.
| I. | In a Coal Mine | 1 |
| II. | Down in the Quarries | 11 |
| III. | Houses of Sand | 21 |
| IV. | Bricks, their Faults and their Virtues | 31 |
| V. | At the Gold Diggings | 39 |
| VI. | The Story of a Silver Mine | 48 |
| VII. | Iron, the Everyday Metal | 57 |
| VIII. | Our Good Friend Copper | 65 |
| IX. | The New Metal, Aluminum | 76 |
| X. | The Oil in our Lamps | 84 |
| XI. | Little Grains of Salt | 95 |
| A STRUCTURAL STEEL APARTMENT BUILDING | vi |
| HOW A COAL MINE LOOKS ABOVEGROUND | 5 |
| MINERS AND THEIR MINE | 10 |
| OPENING A GRANITE QUARRY | 13 |
| BUILDING A CONCRETE ROAD | 27 |
| IN A NEW JERSEY BRICK MILL | 33 |
| HYDRAULIC GOLD MINING | 41 |
| THE STORY OF A SPOON | 51 |
| IN THE STEEL FOUNDRY | 61 |
| IN A COPPER SMELTER | 67 |
| A "MOVIE" OF AN ALUMINUM FUNNEL | 79 |
| A CALIFORNIA OIL FIELD | 87 |
 A STRUCTURAL STEEL APARTMENT BUILDING
A STRUCTURAL STEEL APARTMENT BUILDING
Courtesy American Bridge Co.
First the steel frame, then the floors, then the stone or brick shell,
then the interior finishing—this is how the building is made.
Did you ever wonder how beds of coal happened to be in the earth? This is their story.
Centuries ago, so many thousand centuries that even the most learned men can only guess at their number, strange things were coming to pass. The air was so moist and cloudy that the sun's rays had hard work to get through. It was warm, nevertheless, for the crust of the earth was not nearly so thick as it is now, and much heat came from the earth itself. Many plants and trees grow best in warm, moist air; and such plants flourished in those days. Some of their descendants are living now, but they are dwarfs, while their ancestors were giants. There is a little "horse-tail" growing in our meadows, and there are ferns and club mosses almost everywhere. These are some of the descendants; but many of their ancestors were forty or fifty feet high. They grew very fast, especially in swamps; and when they died, there was no lack of others to take their places. Dead leaves fell and heaped up around them.[Pg 2] Stumps stood and decayed, just as they do in our forests to-day. Every year the soft, black, decaying mass grew deeper. As the crust of the earth was so thin, it bent and wrinkled easily. It often sank in one place and rose in another. When these low, swampy places sank, water rushed over them, pressing down upon them with a great weight and sweeping in sand and clay. Now, if you burn a heap of wood in the open air, the carbon in the wood burns and only a pile of ashes remains. "Burning" means that the carbon in the wood unites with the oxygen gas in the air. If you cover the wood before you light it, so that only a little oxygen reaches it, much of the carbon is left, in the form of charcoal.
When wood decays, its carbon unites with the oxygen of the air; and so decay is really a sort of burning. In the forests of to-day the leaves, and at length the trees themselves, fall and decay in the open air; but at the time when our coal was forming, the water kept the air away, and much carbon was left. This is the way coal was made. Some of the layers, or strata, are fifty or sixty feet thick, and some are hardly thicker than paper. On top of each one is a stratum of sandstone or dark-gray shale. This was made by the sand and mud which were brought in by the water. These shaly rocks split easily into sheets and show beautiful fossil impressions of ferns. There are also impressions of the bark and fruit of trees, together with shells, crinoids, corals, remains of fishes and flying lizards, and some few trilobites,—crablike animals with a shell somewhat[Pg 3] like the back of a lobster, but marked into three divisions or lobes, from which its name comes.
Since the crust of the earth was so thin and yielding, it wrinkled up as the earth cooled, much as the skin of an apple wrinkles when the apple dries. This brought some of the strata of coal to the surface, and after a while people discovered that it would burn. If a vein of coal cropped out on a man's farm, he broke some of it up with his pickaxe, shoveled it into his wheelbarrow, and wheeled it home. After a while hundreds of thousands of people wanted coal; and now it had to be mined. In some places the coal stratum was horizontal and cropped out on the side of a hill, so that a level road could be dug straight into it. In other places the coal was so near the surface that it could be quarried under the open sky, just as granite is quarried. Generally, however, if you wish to visit a coal mine, you go to a shaft, a square, black well sometimes deeper than the height of three or four ordinary church steeples. You get into the "cage," a great steel box, and are lowered down, down, down. At last the cage stops and you are at the bottom of the mine. The miners' faces, hands, overalls, are all black with coal dust. They wear tiny lamps on their caps, and as they come near the walls of coal, it sparkles as it catches the light. Here and there hangs an electric lamp. It is doing its best to give out light, but its glass is thick with coal dust. The low roof is held up by stout wooden timbers and pillars of coal. A long passageway stretches off into a blacker darkness than you[Pg 4] ever dreamed of. Suddenly there is a blaze of red light far down the passage, a roar, a medley of all sorts of noises,—the rattling of chains, the clattering of couplings, the shouts of men, the crash of coal falling into the bins. It is a locomotive dragging its line of cars loaded with coal. In a few minutes it rushes back with empty cars to have them refilled.
All along this passageway are "rooms," that is, chambers which have been made by digging out the coal. Above them is a vast amount of earth and rock, sometimes hundreds of feet in thickness. There is always danger that the roof will cave in, and so the rooms are not made large, and great pillars of coal are left to hold up the roof.
Not many years ago the miner used to do all the work with his muscles; now machines do most of it. The miner then had to lie down on his side near the wall of coal in his "room" and cut into it, close to the floor, as far as his pickaxe would reach. Then he bored a hole into the top of the coal, pushed in a cartridge, thrust in a slender squib, lighted it, and ran for his life. The cartridge exploded, and perhaps a ton or two of coal fell. The miner's helper shoveled this into a car and pushed it out of the room to join the long string of cars.
 HOW A COAL MINE LOOKS ABOVEGROUND
HOW A COAL MINE LOOKS ABOVEGROUND
All that shows on the surface is the machinery shed where
the various engines work to keep the air fresh, and bring
up the miners and the coal.
That is the way mining used to be done. In these days a man with a small machine for cutting coal comes first. He puts his cutter on the floor against the wall of coal and turns on the electricity. Chip, chip, grinds the machine, eating its way swiftly into the coal, and soon there is a deep cut all along the[Pg 6] side of the room. The man and his machine go elsewhere, and the first room is left for its next visitors. They come in the evening and bore holes for the blasting. Once these holes were bored by hand, but now they are made with powerful drills that work by compressed air. A little later other men come and set off cartridges. In the morning when the dust has settled and the smoke has blown away, the loaders appear with their shovels and load the coal into the cars. Then it is raised to the surface and made ready for market.
Did you ever notice that some pieces of coal are dull and smutty, while others are hard and bright? The dull coal is called bituminous, because it contains more bitumen or mineral pitch. This is often sold as "run-of-mine" coal,—that is, just as it comes from the mine, whether in big pieces or in little ones; but sometimes it is passed over screens, and in this process the dust and smaller bits drop out.
The second kind of coal, the sort that is hard and bright, is anthracite. Its name is connected with a Greek word meaning ruby. It burns with a glow, but does not blaze. Most of the anthracite coal is used in houses, and householders will not buy it unless the pieces are of nearly the same size and free from dirt, coal dust, and slate. The work of preparation is done in odd-shaped buildings called "breakers." One part of a breaker is often a hundred or a hundred and fifty feet in height. The coal is carried to the top of the breaker. From there it makes a[Pg 7] journey to the ground, but something happens to it every little way. It goes between rollers, which crush it; then over screens, through which the smaller pieces fall. Sometimes the screens are so made that the coal will pass over them, while the thin, flat pieces of slate will fall through. In spite of all this, bits of coal mixed with slate sometimes slide down with the coal, and these are picked out by boys. A better way of getting rid of them is now coming into use. This is to put the coal and slate into moving water. The slate is heavier than the coal, and sinks; and so the coal can easily be separated from it. Dealers have names for the various sizes of coal. "Egg" must be between two and two and five eighths inches in diameter; "nut" between three fourths and one and one eighth inches; "pea" between one half and three fourths of an inch.
Mining coal is dangerous work. Any blow of the pickaxe may break into a vein of water which will burst out and flood the mine. The wooden props which support the roof may break, or the pillars of coal may not be large enough; and the roof may fall in and crush the workers. There are always poisonous gases. The coal, as has been said before, was made under water, and therefore the gas which was formed in the decaying leaves and wood could not escape. It is always bubbling out from the coal, and at any moment a pickaxe may break into a hole that is full of it. One kind of gas is called "choke-damp," because it chokes or suffocates any one who breathes it. There is also "white-damp," the gas which you[Pg 8] see burning with a pretty blue flame over a hot coal fire. Worst of all is the "fire-damp." If you stir up the water in a marsh, you will see bubbles of it rise to the surface. It is harmless in a marsh, but quite the opposite in a mine. When it unites with a certain amount of air, it becomes explosive, and the least bit of flame will cause a terrible explosion. Even coal dust may explode if the air is full of it, and it is suddenly set in motion by too heavy a blast of powder.
Miners used to work by candlelight. Every one knew how dangerous this was; but no one found any better way until, about a hundred years ago, Sir Humphry Davy noticed something which other people had not observed. He discovered that flame would not pass through fine wire gauze, and he made a safety lamp in which a little oil lamp was placed in a round funnel of wire gauze. The light, but not the flame, would pass through it; and all safety lamps that burn oil have been made on this principle. The electric lamp, however, is now in general use. The miner wears it on his cap, and between his shoulders he carries a small, light storage battery. Even with safety lamps, however, there are sometimes explosions. The only way to make a mine at all safe from dangerous gases is to keep it full of fresh, pure air. There is no wind to blow through the chambers and passages, and therefore air has to be forced in. One way is to keep a large fire at the bottom of the air shaft. If you stand on a stepladder, you will feel that the top of the room is much[Pg 9] warmer than the floor. This is because hot air rises; and in a mine, the hot air over the fire rises and sucks the foul air and gas out of the mine, and fresh air rushes in to take its place. Another way is by a "fan," a machine that forces fresh air into the mine.
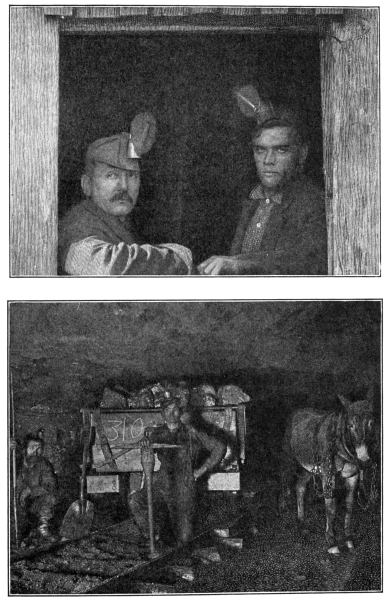 MINERS AND THEIR MINE
MINERS AND THEIR MINE
Notice the safety lamps in the men's caps, and the little railroad
on which the cars of coal and ore travel, hauled by the useful mule.
So it is that by hard work and much danger we get coal for burning. Now, coal is dirty and heavy. A coal fire is hard to kindle and hard to put out, and the ashes are decidedly disagreeable to handle. And after all, we do not really burn the coal itself, but only the gas from it which results from the union of carbon and oxygen. In some places natural gas, as it is called, which comes directly from some storehouse in the ground, is used in stoves and furnaces and fireplaces for both heating and cooking; and perhaps before long gas will be manufactured so cheaply and can be used so safely and comfortably that we shall not have to burn coal at all, but can use gas for all purposes—unless electricity should take its place.
When walking in the country one day I came to a beautiful pond by the side of the road. The water was almost as clear as air, and as I looked down into it, I could see that the bottom was made of granite. The farther shores were cliffs of clean granite thirty or forty feet high and coming down to the water's edge. The marks of tools could be seen on them, showing where blocks of stone had evidently been split off. I picked up a piece of the rock and examined it closely. It proved to be made up of three kinds of material. First, there were tiny sparkling bits of mica. In some places there are mica mines yielding big sheets of this curious mineral which is used in the doors of stoves and the little windows of automobile curtains. With the point of a knife the bits in my piece of granite could be split into tiny sheets as thin as paper. The second material was quartz. This was grayish-white and looked somewhat like glass. The third material was feldspar. This, too, was whitish, but one or two sides of each bit were flat, as if they had not been broken, but split. This is the most common kind of granite. There are many varieties. Some of them are almost white, some dark gray, others pale pink, and yet others deep red. It is found in more than half the States of the Union.[Pg 12]
This quarry had been given up and allowed to fill with water; but it was a granite country, and farther down the road there was another, where scores of men were hard at work. This second quarry was part-way up a hill; or rather, it was a hill of granite which men were digging out and carrying away. When they began to open the quarry, much of the rock was covered with dirt and loose stones, and even the granite that showed aboveground was worn and broken and stained. This is called "trap rock." The easiest way to get rid of it is to blast with dynamite and then carry away the dirt and fragments. Next comes the getting out of great masses of rock to use, some of them perhaps long enough to make the pillars of a large building.
 OPENING A GRANITE QUARRY
OPENING A GRANITE QUARRY
Courtesy Jones Brothers Company.
The first thing to do is to strip off the soil from the stone. Then,
as the blocks are cut out, the big derrick lifts and loads them on
waiting cars.
Now, granite is a hard stone, but there is no special difficulty in cutting it if you know how. In the old days, when people wished to split a big boulder, they sometimes built a fire beside it, and when it was well heated, they dropped a heavy iron ball upon it. King's Chapel in Boston was built of stone broken in this way. To break from a cliff, however, a block of granite big enough to make a long pillar is a different matter, and this is what the men were doing. First of all, the foreman had examined the quarry till he had found a stratum of the right thickness. He had marked where the ends were to come, and the men had drilled holes down to the bottom of the stratum. Then he had drawn a line at the back along where he wished the split to be, and the men had drilled on this line also a row[Pg 14] of holes. Next came the blasting. If one very heavy charge had been exploded, it would probably have shattered the whole mass, or at any rate have injured it badly. Instead of this, they put into each hole a light charge of coarse powder and covered it with sand. These were all fired at the same instant, and thus the great block was loosened from the wall. Sometimes there seems to be no sign of strata, and then a line of horizontal holes must be drilled where the bottom of the block is to be. After this comes what is called the "plug-and-feather" process. Into each hole are placed two pieces of iron, shaped like a pencil split down the middle. These are the "feathers." The "plug" is a small steel wedge that is put between the iron pieces. Then two men with hammers go down the line and strike each wedge almost as gently as if it was a nut whose kernel they were afraid of crushing. They go down the line again, striking as softly as before. Then, if you look closely, you can see a tiny crack between the holes. There is more hammering, the crack stretches farther, a few of the wedges are driven deeper and the others drop out. The block splits off. A mighty chain is then wound about it, the steam derrick lifts it, lays it gently upon a car, and it is carried to the shed to be cut into shape, smoothed, and perhaps polished.
In almost every kind of work new methods are invented after a while. In quarrying, however, the same old methods are in use. The only difference is that, instead of the work being done by muscle, it is[Pg 15] done by compressed air or steam or electricity. Compressed air or steam works the drill and the sledgehammer. The drill is held by an arm, but the arm is a long steel rod which is only guided by the workman. Not the horse-sweep of old times, but the steam derrick and the electric hoist lift the heavy blocks from the quarry. Polishing used to be a very slow, expensive operation, because it was all done by the strength of some one's right arm, but now, although it takes as much work as ever, this work is done by machinery. To "point" a piece of stone, or give it a somewhat smooth surface, is done now with tools worked by compressed air. After this, the stone is rubbed—by machinery, of course—with water and emery, then by wet felt covered with pumice or polishing putty. A few years ago two young Vermonters invented a machine that would saw granite. This saw has no teeth, but only blades of iron. Between these blades and the piece of granite, however, shot of chilled steel are poured; and they do the real cutting.
Granite has long been used in building wherever a strong, solid material was needed; but until the sand blast was tried, people thought it impossible to do fine work in this stone. There was a firm in Vermont, however, who believed in the sand blast. They had a contract with the Government to furnish several thousand headstones for national cemeteries. Cutting the names would be slow and costly; so they made letters and figures of iron, stuck them to the stones, and turned on the blast. If a sand[Pg 16] blast is only fast enough, it will cut stone harder than itself. The blast was turned upon a stone for five minutes. Then the iron letters were removed. There stood in raised letters the name, company, regiment, and rank of the soldier, while a quarter of an inch of the rest of the stone, which the iron letters had not protected, had been cut away. By means of the sand blast it has become possible to do beautiful carving even in material as hard as granite.
Granite looks so solid that people used to think it was fireproof; but it is really poor material in a great fire. Most substances expand when they are heated; but the three substances of which granite is made do not expand alike, and so they tend to break apart and the granite crumbles.
A marble quarry is even more interesting than a granite quarry. If you stand on a hill in a part of the country where marble is worked, you will see white ledges cropping out here and there. The little villages are white because many of the houses are built of marble. Then, too, there are great marble quarries flashing in the sunshine. Sometimes a marble quarry is chiefly on the surface. Sometimes the marble stretches into the earth, and the cutting follows it until a great cavern is made, perhaps two or three hundred feet deep. A roof is often built to keep out the rain and snow. It keeps out the light, too, and on rainy days the roof, together with the smoke and steam of the engines, makes the bottom of the quarry a gloomy place. Everywhere there are slender ladders with men running up and down[Pg 17] them. There are shouts of the men, clanking of chains, and puffing of locomotives.
Marble is cut out in somewhat the same way as granite, but a valuable machine called a "channeler" is much used. This machine runs back and forth, cutting a channel two inches wide along the ends and back and sometimes the bottom of the block to be taken out.
Marble is so much softer than granite that it is far more easy to work. Cutting it is a simple matter. The saw, which is a smooth flat blade of iron, swings back and forth, while between it and the marble sand and water are fed. It does not exactly cut, but rubs, its way through. The round holes in the tops of washstands are cut by saws like this, only bent in the form of a cylinder and turned round and round, going in a little deeper at each revolution. A queer sort of saw is coming into use. It is a cord made of three steel wires twisted loosely together. This cord is stretched tightly over pulleys and moves very rapidly. Every little ridge of the cord strikes the stone and cuts a little of it away.
There are varieties of marble without end. The purest and daintiest is the white of which statues are carved; but there are black, red, yellow, gray, blue, green, pink, and orange in all shades. Many are beautifully marked. The inner walls of buildings are sometimes covered with thin slabs of marble. These are often carefully split, and the two pieces put up side by side, so that the pattern on one is reversed on the other. Certain kinds of marble contain[Pg 18] fossils or remains of coral and other animals that lived hundreds of thousands of years ago. In some marbles there are so many that the stone seems to be almost made of them. When a slab is cut and polished, the fossils are of course cut into; but even then we can sometimes see their shape. One of the most common is the crinoid. This was really an animal, but it looked somewhat like a closed pond lily with a long stem, and people used to call it the stone lily. This stem is made up of little flat rings looking like bits of a pipestem. The stems are often broken up and these bits are scattered through the marble. The animals whose shells help to make marble lived in the ocean, and when they died sank to the bottom. Many of the shells were broken by the beating of the waves, but both broken shells and whole ones became united and hardened into limestone, one kind of which we call marble. Common chalk is another kind. Blackboard crayons are made of this: so are whitewash and whiting for cleaning silver and making putty.
Another stone that builders would be sorry to do without is slate. This, too, was formed at the bottom of the sea. Rivers brought down fine particles of clay, which settled, were covered by other matter, and finally became stone. It was formed in layers, of course, but, queerly enough, it splits at right angles to its bottom line. Just why it does this is not quite certain, but the action is thought to be due to heat and long, slow pressure, which will do wonderful things, as in the case of coal. This splitting[Pg 19] is a great convenience for the people who want to use it for roofing and for blackboards. Blocks of slate are loosened by blasting, and are taken to the splitting-shed.
Splitting slate needs care, and a man who is not careful should never try to work in a slate quarry. The splitting begins by one man's dividing the block into pieces about two inches thick and somewhat larger than the slates are to be when finished. The way he does this is to cut a little notch in one end of the block with his "sculpin chisel" and make a groove from this across the block. He must then set his chisel into the groove, strike it with a mallet, and split the slate to the bottom. This sounds easy, but it needs skill. Slate has sometimes its own notions of behavior, and it does not always care to split in a straight line exactly perpendicular to the bottom of the stratum. The man keeps it wet so that he can see the crack more plainly, and if that crack turns back a little to the right, he must turn it to the left by striking the sculpin toward the left, or perhaps by striking a rather heavy blow on the left of the stone itself. Now the chief splitter takes it, and with a broad thin chisel he splits it into plates becoming thinner at each split. The second assistant trims these into the proper shape and size with either a heavy knife or a machine. Slate can be sawed and planed; but whatever is done to it should be done when it first comes from the quarry, for then it is not so likely to break. It would be very much cheaper if so much was not broken and wasted[Pg 20] at the quarries and in the splitting. It is said that in Wales sometimes one hundred tons of stone are broken up to get between three and four tons of good slate. Within the last few years the quarrymen have been using channeling machines and getting out the slate in great masses instead of small blocks. This is not so wasteful by any means; but even now there is room for new and helpful inventions.
If you wanted to build a house, of what should you build it? In a new country, people generally use wood; but after a time wood grows expensive. Moreover, wood catches fire easily; therefore, as a country becomes more thickly settled and people live close together in cities, stone and brick are used. Large cities do not allow the building of wooden houses within a certain distance from the center, and sometimes even the use of wooden shingles is forbidden. Of late years large numbers of "concrete" or "cement" houses have been built. Our grandfathers would have opened their eyes wide at the suggestion of a house built of sand, and would have felt anxious at every rainfall lest their homes should suddenly melt away. Even after thousands of concrete buildings were in use, many people still feared that they would not stand the cold winters and hot summers of the United States; but it has been proved that concrete is a success provided it is properly made.
No one can succeed in any work unless he understands how it should be done. Concrete is made of Portland cement, mixed with sand and water and either broken stone, gravel, cinders, or slag; but if any one thinks that he can mix these together without knowing how and produce good concrete, he[Pg 22] will make a bad mistake rather than a good building material.
First, he must buy Portland cement of the best quality. This cement is made of limestone and clay, or marl, chalk, and slag. These are crushed and ground and put into a kiln which is heated up to 2500° or 3000°F.; that is, from twelve to fourteen times as hot as boiling water. The stone fuses sufficiently to form a sort of clinker. After this has cooled, it is ground so fine that the greater part of it will pass through a sieve having 40,000 meshes to the square inch. To every hundred pounds of this powder, about three pounds of gypsum is added. The mixture is then put into the bags in which we see it for sale in the stores. This powder is so greedy for water that it will absorb the moisture from the air around it. Even in the bags, it begins to harden as soon as it gets some moisture; and as soon as it hardens, it is of no use. The moral of that is to keep your cement in a dry place.
The second substance needed in concrete is broken stone or gravel. Of course a hard rock must be selected, such as granite or trap rock. Limestone calcines in a heat exceeding 1000° F., and therefore it cannot be used in fireproof construction. Soft rock, like slate or shale or soft sandstone, will not answer because it is not strong enough. Gravel is always hard. If you look at a cut in a gravel bank, you will usually see strata of sand and then strata of rounded pebbles of different sizes. The sand was once an ancient sea beach; the pebbles were dashed[Pg 23] up on it by waves or storms or some change of currents. They were at first only broken bits of rock, but after being rolled about for a few thousand years in the ocean and on the shore, the corners were all rounded. Soft rock would have been ground to powder by such treatment. Sometimes, if there is to be no great strain on the concrete, cinders or pieces of brick may be used instead of stone; and for some purposes they answer very well.
The third substance used in concrete is sand; but it must be the right kind of sand, having both fine and coarse grains. These grains need to be sharp, or the cement will not stick to them well. They must also be clean, that is, free from dirt. If you rub sand between your hands, and it soils them, then there is clay or loam with it, and it must not be used in making concrete unless it is thoroughly washed. Another way of testing it is to put it into a glass jar partly full of water and shake it. Then let it settle. If there is soil in the sand, it will appear as a stratum of mud on top of the sand.
The water with which these three substances are to be mixed must be clean and must contain no acid and no strong alkali. As a general rule, there must be twice as much broken stone as sand. When people first make concrete, they often expect too much of their materials. A good rule for the strongest sort of cement, strong enough for floors on which heavy machines are to stand, is one fourth of a barrel of cement, half a barrel of sand, and one barrel of gravel or broken stone. Apparently this would make[Pg 24] one and three fourths barrels; but in reality it makes only about one barrel, because the sand fills in the spaces between the gravel, and the cement fills in the spaces between the grains of sand.
There are many sorts of machines on the market for mixing the materials; but small quantities can just as well be mixed by hand. The "mixing-bowl" is a platform, and on this the sand is laid. Then comes the cement; and these two must be shoveled together several times. While this is being done, the broken stone or gravel must be wet, and now it is put on top of the sand and cement and well shoveled together, with just enough water added so that the mass will almost bear the weight of a man.
Concrete is impatient to be hardening, and if it is not put into the right place, it will begin promptly to harden in the wrong place, and nothing can be done with it afterwards. If it is to be made in blocks, the moulds must be ready and the concrete put into them at once and well tamped down. For such uses as beams and the sides of tanks where great strength is needed, the cement is often "reinforced," that is, rods of iron or steel are embedded in it. For floors, a sheet of woven wire is often stretched out and embedded. At first only solid blocks, made to imitate rough stone, were used for houses, but the hollow block soon took their place. This is cheaper; houses built this way are warmer in winter and cooler in summer; and it prevents moisture from working through the walls. Many cities have regulations about the use of hollow[Pg 25] blocks, all the more strict because concrete is comparatively new as a building material. In Philadelphia the blocks must be composed of at least one barrel of Portland cement to five barrels of crushed rock or gravel. They must be three weeks old or more before being used; the lintels and sills of the doors must be reinforced; and every block must be marked, so that if the building should not prove to be of proper strength, the maker may be known. There would seem, however, to be little question of the quality of the blocks, for samples must pass the tests of the Bureau of Building Inspection.
Even better than the hollow block is the method of making the four walls of a house at once by building double walls of boards and pouring in the concrete. When this has hardened, the boards are removed, and whatever sort of finish the owner prefers is given to the walls. They can be treated by spatter-work, pebble dash, or in other ways before the cement is fully set, or by bush hammering and tool work after the cement has hardened. Coloring matter can be mixed with the cement in the first place; and if the owner decides to change the color after the house is completed, he can paint it with a thin cement of coloring matter mixed with plaster of Paris.
A concrete house has several advantages. In the first place, it will not burn. Neither will granite, but granite will fall to pieces in a hot fire. Granite is made of quartz, mica, and feldspar, as has been said before. These three do not expand alike in heat;[Pg 26] and therefore great flakes of the stone split off, so that it really seems to melt away. A well-made concrete is not affected by fire. It will not burn, and it will not carry heat to make other things burn. For a concrete house no paint is needed and less fuel will be required to keep it warm. If the floors are made with even a very little slant, "house-cleaning" consists of removing the furniture and turning on the hose. Water-tank, sink, washtubs, and bathtubs can be cast in concrete and given a smooth finish. Wooden floors can be laid over the concrete, or a border of wood can be put around each room for tacking down carpets or rugs. A concrete house may be as ornamental as the owner chooses, for columns and cornices and mouldings can easily be made of concrete; and if they are cast in sand, as iron is, they will have a finish like sandstone.
It is somewhat troublesome to lay concrete in very cold weather, because of the danger of freezing and cracking. Sometimes the materials are heated, and after the concrete is in place, straw or sand or sawdust is spread over it. These will keep it warm for several hours, and so give the concrete a chance to "set." Sometimes a canvas house is built over the work. When a concrete dam was to be built in the Province of Quebec and the mercury was 20° below zero, the contractors built a canvas house over one portion of the dam and set up iron stoves in it. When this part was completed, they took down the house and built it up again over another portion of the dam. Sometimes salt is used. Salt water is heavier than fresh water and will not freeze so easily. Therefore salt put into the water used in making the concrete will enable it to endure more cold without freezing; but not more than one pound of salt to twelve gallons of water should be used.
 BUILDING A CONCRETE ROAD
BUILDING A CONCRETE ROAD
Courtesy Alpha Portland Cement Co.
The concrete mixer travels along the prepared roadbed, and after it
follow the workmen with levelers and stamps.
Concrete objects to being frozen before it is "set," but it is exceedingly accommodating about working under water. It must, of course, be carried in some way through the water to its proper place without being washed away, but this is easily done. Sometimes it is let down in great buckets closed at the top, but with a hinged bottom that will open when the bucket strikes the rock or soil where the material is to be left. Sometimes it is poured down through a tube. Sometimes it is dropped in sacks made of cloth. This cloth must be coarse, so that enough of the concrete will ooze through it to unite the bag and its contents with what is below it and make a solid mass. Sometimes even paper bags have been successfully used. The concrete, made rather dry, is poured into the bags and they are slid down a chute. The paper soon becomes soft and breaks, and lets the concrete out. Sometimes concrete blocks are moulded on land and lowered by a derrick, while a diver stands ready to see that they go into their proper places.
Concrete is used for houses, churches, factories, walls, sidewalks, steps, foundations, sewers, chimneys, piers, cellar bottoms, cisterns, tunnels, and even bridges. In the country, it is used for silos,[Pg 29] barn floors, ice houses, bins for vegetables, box stalls for horses, doghouses, henhouses, fence posts, and drinking-troughs. It is of very great value in filling cavities in decaying trees. All the decayed wood must be cut out, and some long nails driven from within the cavity part-way toward the outside, so as to help hold the concrete. Then it is poured in and allowed to harden. If the cavity is so large that there is danger of the trunk's breaking, an iron pipe may be set in to strengthen it. If this is encased in concrete, it will not rust. A horizontal limb with a large cavity may be strengthened by bending a piece of piping and running one part of it into the limb and the other into the trunk, then filling the whole cavity with concrete. If the bark is trimmed in such a way as to slant in toward the cavity, it will sometimes grow entirely over it.
Concrete is also used for stucco work, that is, for plastering the outside of buildings. If the building to be stuccoed is of brick or stone, the only preparation needed is to clean it and wet it; then put on the plaster between one and two inches thick. A wooden house must first be covered with two thicknesses of roofing-paper, then by wire lathing. The concrete will squeeze through the lathing and set. Stucco work is nothing new, and if it is well done, it is lasting.
Concrete has been used for many purposes besides building, and the number of purposes increases rapidly. For blackboards, refrigerator linings, and railroad ties it has been found available, and for[Pg 30] poles or posts of all sizes it has already proved itself a success. It has even been suggested as an excellent material for boats, if reinforced; and minute directions are given by one writer for making a concrete rowboat. To do this, the wooden boat to be copied is hung up just above the ground, and clay built around it, leaving a space between boat and clay as thick as the concrete boat is to be. The wooden boat is covered with paper and greased, then the concrete is poured into the space between the boat and the clay mould; and when it hardens and the wooden boat is removed, there is a boat of stone—or so the directions declare; but I think most people would prefer one of wood. However it may be with rowboats, concrete is taking an important place in the construction of battleships, a backing for armor being made of it instead of teakwood. The Arizona is built in this way.
Concrete that is carelessly made is very poor stuff, and dangerous to use, for it is not at all reliable and may give out at any time; but concrete that is made of the best materials and properly put together is an exceedingly valuable article.
The simplest way to make a brick is to fill a mould with soft clay, then take it out and let it stiffen, and then put it in the sun to dry. This is the way in which the "adobe" bricks of Central America are made. They answer very well in countries where there is little rain; but one or two heavy downpours would be likely to melt a house built of such material.
Clay is a kind of earth containing mostly alumina and silica or sand, that can be mixed with water, moulded into any shape, retain that shape after it is dry, and become hard by being burned. If you want to make a china cup, you must have a fine sort of clay called "kaolin," which is pure white when it is fired and is not very common; but if you want to make bricks, it will not be at all difficult to find a suitable clay bank. And yet the clay, even for bricks, must be of the right kind. If it contains too much silica (sand), the brick will not mould well; if too much alumina it will be weak; if too much iron, it will lose its shape in burning; if too much lime, it will be flesh-colored when it is burned.
If you want to find out whether a building-brick is of good quality, there are some tests that a boy or girl can apply as well as any one. First, look the brick over and note whether it is straight and true,[Pg 32] and whether the edges and corners are sharp. Strike it, and see whether it gives a clear, ringing sound. Then weigh it and soak it in water for twenty-four hours. Weigh it again, and if it is more than one fifth heavier than it was before soaking, it is not of the first quality.
After the clay has been dug, it must be "tempered," that is, mixed with water and about one third or one fourth as much sand as clay, and left overnight in a "soak pit," a square pit about five feet deep. In the morning the workmen shovel the mass over and feed it into the machines for forming the bricks. The mixing is better done, however, in a "ring pit." This is a circular pit twenty-five or thirty feet in diameter, three feet deep, and lined with boards or brick. A big iron wheel works from the center to the edge and back again for several hours, through and through the clay. A method even better than this is to put the clay and sand and water into a great trough, in which there is a long shaft bristling with knives. The shaft revolves, mixes the clay, and pushes it along to the end of the trough. This is called "pugging," and the whole thing—trough, shaft, and knives—is a "pug mill."
In the old days bricks were always made by hand. The moulder stood in front of a wet table whereon lay a heap of soft clay. He either wet or sanded his mould to keep it from sticking. Meanwhile, his assistant had cut a piece of clay and rolled it and patted it into the shape of the mould. In making bricks, there can be no patching; the mould must be filled at one stroke, or else there will be folds in the brick. To make a good brick, the moulder lifts the clay up above his head and throws it into the mould with all his force. Then he presses it into the corners with his thumbs, scrapes off with a strip of wood any extra clay, or cuts it off with a wire, smooths the surface of the brick, puts mould and brick upon a board, jerks the mould up and proceeds to make another brick.
 IN A NEW JERSEY BRICK MILL
IN A NEW JERSEY BRICK MILL
Copyright by Underwood and Underwood.
This man is moulding a fire-brick to its final shape.
No matter how expert a moulder may be, brick-making by hand is slow work, and in most places machines are used. In what is called the "soft-mud" process, the clay is pushed on by the pug mill to the end of the trough. There stands a mould for six bricks. A plunger forces the clay into it, the mould is emptied, and in a single hour five thousand bricks can be made. By what is called the "stiff-mud" process, the stiff clay is put into a machine with an opening the size of the end or side of a brick. The machine forces the clay through this opening, cuts it off at the proper moment; and so makes bricks by the thousand without either mould or moulder. A third way of making brick is by what is called the "dry process." The clay is pulverized and filled into moulds the length and breadth of a brick, but much deeper, and with neither top nor bottom. One plunger from above and another from below strike the clay in the mould with much force, and make the fine, smooth brick known as "pressed brick." All this is done by machinery, and some machines[Pg 35] make six bricks at a time. These "dry" bricks are fragile before they are burned, and must be handled with great care.
Bricks cannot be put into the kiln while they are still wet, for when a brick is drying, it is a delicate article. It objects to being too hot or too cold, and it will not stand showers or drafts. In some way about a pound of water must be dried out of each brick; but if you try to hurry the drying, the brick turns sulky, refuses to have anything more to do with you, and proceeds to crack. To dry, bricks are sometimes spread on floors; or piled up in racks on short pieces of board called "pallets"; and sometimes they are put upon little cars and run slowly through heated tunnels. The last is the best way for people who are in a hurry, for it takes only from twenty-four to thirty-six hours to make the bricks ready to go to the kiln to be burned.
In one sort of kiln, the bricks themselves make the kiln. They are piled up in arches, but left a little way apart so the hot air can move freely among them. The sides of the structure are covered with burnt brick and mud, but the top is left open to allow the steam from the hot bricks to escape. The fires are in flues that are left at the bottom. They must burn slowly at first, but after a while, some forty to sixty hours, the heat becomes intense. Thus far the bricks have been grayish or cream-colored, but now, if there is iron in them, they turn red; if there is lime, they turn yellow; if a large amount of lime, they become flesh-colored. Besides[Pg 36] this sort of kiln, which is torn down when the bricks are sufficiently burned, there is also the permanent kiln, which has fixed side walls and either an open or closed top. Then, too, there is a "continuous" kiln. This has a number of chambers, and the heat from each one passes into the next; so that bricks in one chamber may be just warming up while in another they are ready to be taken out.
When the bricks come out of the kiln, some of them are good and some are not. Those that were on the outside are not burned enough; those next it are not well baked, but can be used for the middle of thick walls. The next ones are of good quality; but those directly over the fires are so hard and brittle that they are of little use except for pavements.
Paving-bricks, however, are not to be despised. They are not as smooth and well finished as pressed brick, but they are exceedingly useful. They need as much care in making as any others, and they must be burned in a much hotter fire to make them dense and hard. The tests for paving-bricks are quite different from those for ordinary building-brick. If first-class paving-bricks weighing fifty pounds are soaked in water for twenty hours, they take up so little water that they will not weigh more than fifty-one or fifty-one and a half pounds when taken out. To find out how hard they are, the bricks are weighed and shaken about with foundry shot for a number of hours. Then they are weighed again to see how much of their material has been rubbed off. A third test is to put one[Pg 37] brick on edge into a crushing machine to see how much pressure it will stand. Paving-brick is cheaper than granite blocks, and if it has a good foundation of concrete covered with sand, it will last about three fourths as long. Brick is less noisy than stone and is easier to clean.
Not so very long ago, when particularly handsome bricks were needed for the outside of walls and other places where they would be conspicuous, they were "re-pressed"; that is, they were made by hand or in a "soft-mud" machine, and then, after drying for a while, were put into a re-pressing machine to give them a smooth finish. These machines are still used, but they are hardly necessary, for the "dry-clay" brick machine will turn out a smooth brick in one operation.
Another substance which is made of almost the same materials as brick is terra cotta. To make this, fire brick, bits of pottery, partly burned clay, and fine white sand are ground to a powder and mixed very thoroughly. This mixture is moulded, dried, and burned. Until recently, all terra cotta was of the color that is called by that name, but now it is made in gray, white, and bronze as well.
Bricks are laid in mortar, and this makes a wall one solid mass and stronger than it could be without any cement. But mortar does more than this. It is more elastic than brick, and therefore, when a wall settles, the mortar yields a little, and this often prevents the bricks from cracking. Bricks are always thirsty, and if one is laid in mortar, it will[Pg 38] suck the moisture out of it almost as a sponge will suck up water. The mortar thus has no chance to set, and so is not strong as it should be. That is why the bricklayer wets his bricks, especially in summer, before he puts them in place. Lime or cement mortar will not set in freezing weather, and a brick building put up in the winter is in danger of tumbling down when the warm days of spring arrive.
This thirstiness of bricks is their greatest fault. Three or four days of driving rain will sometimes wet through a brick wall two feet thick, crumbling the plaster and spoiling the wallpaper. That is why it is a poor plan to plaster directly on the brick wall of a house. "Furring" strips, as they are called, or narrow strips of wood, should be fastened on first and the laths nailed to these, or the wall can be painted or oiled on the outside. The best way, however, though more expensive, is to build the wall double. Then there is air between the two thicknesses of brick. Air is a poor conductor of heat; so in summer it keeps the heat out, and in winter it keeps it in.
But brick will suck up water from the ground as well as from a storm; and therefore, when a brick house is to be built in a wet place, there ought to be a three-eighths-inch layer of something waterproof, like asphalt and coal tar, put on top of one of the layers of brickwork to prevent the moisture from creeping up.
Bricks have their faults, but they will not burn, and when properly used, they make a most comfortable and enduring house.
When gold was first discovered in California, in 1848, people from all over the world made a frantic rush to get there, every one of them hoping that he would be lucky enough to make his fortune, and fearing lest the precious metal should be gone before he could even begin to dig. The gold that these men gathered came from what were called "placers"; that is, masses of gravel and sand along the beds of mountain streams. Each miner had a pan of tin or iron, which he filled half-full of the gravel, or "pay dirt," as the miners called it. Then, holding it under water, he shook off the stones and mud over the side of the pan, leaving grains of gold mixed with black sand at the bottom. This black sand was iron, and after a while the miners removed it with a magnet, dried what remained, and blew away the dust, leaving only the grains of gold.
Another contrivance which soon came into use was the "cradle." This was a long box, sometimes only a hollowed-out log. At the top was a sieve which sifted out the stones. Nailed to the bottom of the cradle were small cleats of wood, or "riffles," which kept the water from running so fast as to sweep the gold out of the cradle with it. The cradle was placed on rockers and was also tilted slightly. The miner shoveled the gravel into the top of the[Pg 40] cradle and his partner rocked it. The sieve kept back the stones, the water broke up the lumps of earth and gravel and washed them down the cradle, and the grains of gold were stopped by the riffles, and sank to the bottom. Sometimes the "pay dirt" continued under a stream. To get at it, the miners often built a little canal and turned the water into a new channel; then they could work on the former bed of the river.
Before many years had passed, the gold that was near the surface had been gathered. The miners then followed the streams up into the mountains, and found that much of the gold had come from beds where in ancient times rivers had flowed. There was gold still remaining in these beds, but it was poorly distributed, the miners thought. Sometimes there would be quite an amount in one place, and then the miner would dig for days without finding any more. Even worse than this was the fact that these gravel beds were not on the top of the ground, but were covered up with soil and trees. Evidently the slow work with pans and cradles would not pay here; but it occurred to some one that if a powerful stream of water could be directed against the great banks of earth, as water is directed against a burning building, they would crumble, the dirt could be washed down sluices, and the gold be saved. This was done. Great reservoirs were built high up in the mountains, and water was brought by means of ditches or pipes to a convenient place. Then it was allowed to rush furiously through a hose and nozzle, and the great stream coming with tremendous force was played upon the banks of gravel. The banks crumbled, the gravel was washed into a string of sluices, or long boxes with riffles to catch the gold. Soon the miners found that if quicksilver was put into these sluices, it would unite with the gold and make a sort of paste called "amalgam." Then if this amalgam was heated, the quicksilver would be driven off in the form of gas, and the gold would remain in a beautiful yellow mass.
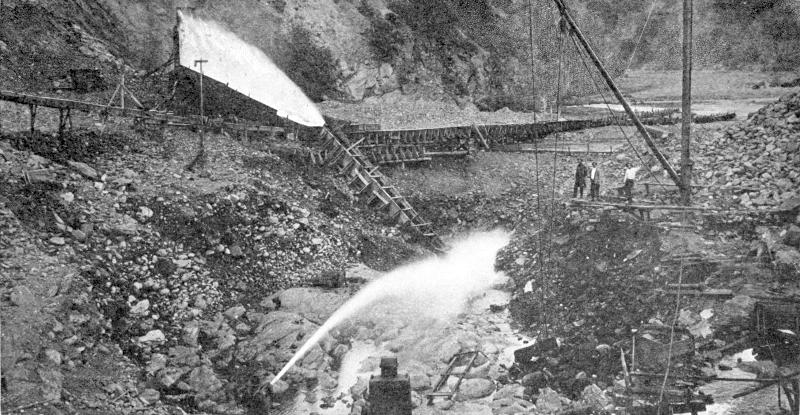 HYDRAULIC GOLD MINING
HYDRAULIC GOLD MINING
A placer mine at Gold Point, California, where tremendous streams of
water under high pressure are busy washing away the side of a
gold-bearing hill.
The ancient rivers had also carried gold to the valleys, and to collect this a dredge, which the miners called a "gold ship," came into use. The "ship" part of this machine is an immense flat scow. Stretching out from one end is something which looks like a moving ladder. This is the support of an endless chain of buckets, each of which can bite into the gravel and take a mouthful of five or six hundred pounds. They drop this gravel into a big drum which is continually revolving. Water flows through the drum, and washes out the sand and bits of gold over large tables, where by means of riffles and quicksilver the gold is captured. This scow was usually on dry land at first; but its digging soon made a lake, and then it floated. It must be more fascinating to hold a pan in your own hands and pick out little grains of gold or perhaps even a big piece of it with your own fingers, but if the gravel is good the dredge makes more money.
In Alaska the great difficulty in mining is that,[Pg 43] except at the surface, the ground is frozen all the year round. At first, the miners used to thaw the place where they wished to dig by building wood fires; but this was a slow method, and now the thawing is done by steam. They carry the steam in a pipe to the place where the digging is to be done, and send it through a hose. At the end of the hose is a pointed steel tube. They hammer this tube into the ground and let some steam pass through the nozzle. This softens the ground so that picks and shovels may be used. There is generally cold enough in Alaska, but once at least the miners had to manufacture it. The gold-bearing gravel was deep, the ground was flat, and it was often overflowed. They set up a freezing plant, and shut in their land with a bulkhead of ice several feet thick. Then they pumped out what water was already in and did their work with no more trouble.
When gold began to grow less in the California gravel, the miners looked for it in the rocks on the mountain-side. The placer miners laughed at them and called their shafts "coyote holes"; but in time the placers failed, while nearly all of our gold to-day comes from veins of white quartz in the rocks. A vein of gold is the most capricious thing in the world. It may be so tiny that it can hardly be seen, then widen and grow rich in gold, then suddenly come to an end. This is why a new mine is so uncertain an enterprise. The gold may hold out and bring fortunes to the investors, or it may fail, and then all they will have to show for their money is the[Pg 44] memory that they put it into a hole in the ground. The managers of a few of the well-established mines, however, have explored so far as to make sure that there is gold enough for many years of digging.
The mining engineer must be a very wide-awake man. It is not enough for him simply to remember what was taught him in the schools of mining; he must be bright enough to invent new ways of meeting difficulties. No two mines are alike, and he must be ready for all sorts of emergencies. A gold mine now consists of a shaft or pit dug several hundred feet down into the rock, with levels or galleries running off from it and with big openings like rooms made where the rock was dug out. The roofs of the rooms are supported by great timbers. To break away the rock, the miner makes a hole with a rock drill worked by electricity or compressed air, puts powder or dynamite into the hole and explodes it. The broken rock is then raised to the surface and crushed in a "stamping mill." Here the ore is fed into a great steel box called a "mortar." Five immense hammers, often weighing a thousand pounds apiece, drop down upon the ore, one after another, until it is fine enough to go through a wire screen in the front of the box. When two hundred or more of these hammers are pounding away with all their might, a stamping mill is a pretty noisy place. The ore, crushed to a fine mud, now runs over sloping tables covered with copper. Sticking to the top of the copper is a film of quicksilver. This holds fast whatever gold there may be and[Pg 45] makes an amalgam, which is scraped off from time to time, and the quicksilver is driven from the gold by heat.
Gold that is not united with other metals is called "free milling gold." Much of it, however, is found in combination with one metal or another, and is known as "rebellious" or "refractory" gold. Such gold may sometimes be set free by heat, and sometimes by chemicals. One way is by the use of chlorine gas, and the story of it sounds almost like "The house that Jack built." It might run somewhat like this: This is the salt that furnishes the chlorine. This is the chlorine gas that unites with the gold. This is the chloride that is formed when the chlorine gas unites with the gold. This is the water that washes from the tank the chloride that is formed when the chlorine gas unites with the gold. This is the sulphate of iron that unites with the chlorine gas of the chloride that the water washes from the tank that is formed when the chlorine gas unites with the gold—and leaves the gold free.
Another method is by the use of cyanide. More than a century ago a chemist discovered that if gold was put into water containing a little cyanide, the gold would dissolve, while quartz and any metals that might be united with the gold would settle in the tank. The water in which the gold is dissolved is now run into boxes full of shavings of zinc and is "precipitated" upon them; that is, the tiny particles of gold in the water fall upon the zinc and cling to it. Zinc melts more easily than gold, so if this gilded[Pg 46] zinc is put into a furnace, the zinc melts and the gold is set free.
Very often gold is found combined with lead or copper. It must then be melted or smelted in great furnaces. The metal is heavier than the rock and settles to the bottom of the furnace. It is then drawn off and the gold is separated from the other metals, usually by electricity.
Sometimes large pieces of gold called "nuggets" are found by miners. The largest one known was found in Australia. It weighed 190 pounds and was worth $42,000. Sometimes spongy lumps of gold are found; but as a general thing gold comes from the little specks scattered through veins in rock, and much work has to be done before it can be made into coins or jewelry. It is too soft for such uses unless some alloy, usually copper or silver, is mixed with it to make it harder. Sometimes it is desirable to know how much alloy has been added. The jeweler then makes a line with the article on a peculiar kind of black stone called a "touchstone," and by the color of the golden mark he can tell fairly well how nearly pure the article is. To be more accurate, he pours nitric acid upon the mark. This eats away the alloy and leaves only the gold.
Gold is a wonderful metal. It is of beautiful color; it can be hammered so thin that the light will shine through it; few acids affect it, and the oxygen which eats away iron does not harm it. Pure gold is spoken of as being "twenty-four carats fine," from carat, an old weight equal to one twenty-fourth of an[Pg 47] ounce troy. Watchcases are from eight to eighteen carats fine; chains are seldom more than fourteen; and the gold coins of the United States are about eleven parts of gold and one of copper. Coins wear in passing from one person to another, and that is why the edges are milled, so that it may be more easily seen when they have become too light to be used as coins. When such pieces come into the hands of the Government, they must be recoined.
A man who goes out in search of a mine is called a "prospector." The best prospector is a man who has learned to keep his eyes open and to recognize the signs of gold and silver and other metals. A faithful friend goes with him, a donkey or mule which carries his bacon and beans, blankets, saucepan, and a few tools, such as a pan, pick, shovel, hammer, and axe. Sometimes the prospector also takes with him a magnifying glass and a little acid to test specimens, but usually he trusts to his eyes alone.
When these few things have been brought together, the prospector and the donkey set out. They wander over the hills and down into the canyons. If a rock is stained red, the prospector examines it to see whether it contains iron; if it is green, he looks for copper. In the canyons and along the creeks he often tests the gravel for traces of some valuable metal. If he finds any of these traces along the stream, he follows them on the bank until they stop; then he carefully examines the bank of the stream or the nearest hillside. If he continues to find bits of metal, they will lead him to a vein of ore, from which they have been broken by the wind, rain, and frost.
Generally a prospector is looking for some one[Pg 49] special metal, and in his search he often overlooks some other metal; for instance, thousands of the gold-seekers who rushed to California in 1849 hurried through Nevada on their way. If they had only known what was under their feet, they would have taken their picks and shovels and begun to dig, instead of trying to get out of the region as soon as might be. Ten years later, the California placers were becoming exhausted, and miners began to go elsewhere in their search for gold.
Among those who were working in what is now the State of Nevada were two Irishmen who had been unlucky in California and had fared no better in Nevada. They wanted to go somewhere else, but they had not money enough for the journey; so they kept on with their work at the foot of Mount Davidson, washing the gravel and saving the little gold that they found. They were annoyed by some heavy black stuff that united with the quicksilver in their cradles, interfered with the saving of the gold, and put them in a very bad temper. At length a man named Henry Comstock came along, who told them that this black stuff was silver ore. They examined the mountain-side, and discovered the outcrop or edge of a great vein containing gold and also silver. It is no wonder that people rushed from the east and west to the wonderful new mines, for it was plain that these new "diggings" were not mere placers, but rich veins that many years of working might not exhaust. Every newcomer hoped to discover a vein; and within a year or two the district[Pg 50] around the Comstock lode was full of deep shafts, many of them abandoned and half-hidden by low brush, but some of them yielding quantities of gold and silver. Before this, there had been only about a thousand people in what is now Nevada, but in two years after the discovery of silver, there were 16,000, and a new Territory was formed.
The miners knew how to get gold out of ore, but silver was another matter, and some of it was difficult to extract. They had so much trouble that they were ready to believe in any treatment of the ore, no matter how absurd, that promised to help them out of their difficulties. Some of them were actually persuaded that the juice of the wild sagebrush would bring the silver out. It is no wonder that they were troubled, for in the Comstock lode were not only gold and silver, but ten or twelve other metals or combinations of silver with something else. At length processes were invented for treating the different kinds of ore. Some kinds were crushed in a stamping mill, then ground to a powder and mixed with quicksilver or mercury. This mercury united with both the gold and the silver, making an amalgam. The amalgam, together with the finely ground ore, was put into a "settler," and here the heavy amalgam sank to the bottom and was then strained. The extra mercury was collected, and the amalgam was put into a retort or kettle and heated. The mercury became a gas and was driven off from the gold and silver, then caught in a vessel cool enough to condense it, just as a cold plate held in steam will collect drops of water. Sometimes the ore was mixed with copper and lead. In that case common salt and copper sulphate were used. Some ore had to be roasted in a furnace in order to drive off the sulphur.
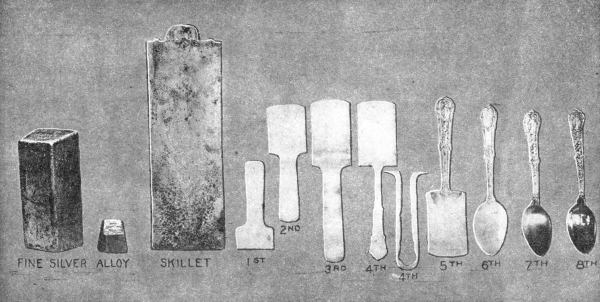 THE STORY OF A SPOON
THE STORY OF A SPOON
Courtesy The Gorham Co.
(1) Silver strip blanked. (2) Pinched. (3) Graded. (4) Outlining of Handle.
(5) Stamped Handle. (6) Spoon completely trimmed. (7, 8) Finished spoons.
There were great and unusual dangers to be met in getting the ore. The vein of quartz which bore it was fifty or sixty feet wide. Some was hard, and some so soft and crumbling that pillars would not hold up the roof. The passageways were then lined with heavy logs standing on either side, other logs laid across their tops, and all bolted firmly together. Nevertheless, they twisted and fell, and slowly but certainly the whole mass of earth and rock, two hundred or more feet in thickness, was coming down upon the heads of the miners. The work on the Comstock mines had come to an end unless a man could be found able to invent some system of support not laid down in the books. The man was found. He took short, square timbers five or six feet long, put them together as if they were the sides and ends of square boxes, and piled them one above another, making hollow pillars. He fastened these firmly together and filled the space inside with waste rock, thus making strong, solid pillars that would support almost any weight that could be put upon them.
There were two other dangers, water and heat. The vein was porous and water was constantly trickling out of it. Then, too, there were "water pockets," or natural reservoirs in the rock, and any[Pg 53] moment the stroke of a pick might let out a torrent and force the miners to run for their lives. Sometimes minerals were dissolved in this water, and the men with closed eyes and swollen faces had to be hurried to the surface for treatment. Powerful pumps had to be used and the water sent away through long lines of pipes. This water was warm, and in very deep workings in the Comstock vein it was boiling hot. Even with quantities of ice sent down to cool them, the men could work in some places only a short time.
In San Francisco there was a mining engineer named Adolph Sutro who planned to remedy these troubles by driving a big four-mile tunnel through the heart of the mountain, letting out the hot water and the foul air. The owners of some of the mines joined him in raising the money, and the tunnel was dug. Through this the water ran out. The mines were freed of foul air and fresh air was driven in.
The Comstock lode has given up an amazing amount of precious metal. Between 1860 and 1890 it produced $340,000,000. After 1890, however, its product grew less. The vein was not so rich, the price of silver fell, while the cost of mining it at great depths increased. Not nearly so much was mined, and at length water rose in the mines up to the level of the Sutro Tunnel. In 1900 new machinery was put in and new methods were adopted, such as treating the tailings with cyanide and so saving much of the precious metal from them. From the beginning the Comstock mines have been so ready[Pg 54] to follow improved methods that they have been called the mining school of the world.
Great quantities of silver are used for making jewelry and for tableware. The one objection to its use is that silver likes to unite with sulphur, and thus the silver easily becomes black. There is sulphur in the yolk of an egg and that is why the spoon with which it has been eaten turns black. Even if silverware is not used, it tarnishes, especially in towns, because there is so much sulphureted hydrogen in the air. In perfectly pure air, it would not tarnish. Silver is harder than gold, but not hard enough to be used without some alloy, usually copper. Tableware is "solid" even if it contains alloy enough to stiffen it. It is "plated" if it is made of some cheaper metal and covered with silver. The old way of doing this was to fasten with bits of solder a thin sheet of silver to the cup or vase or whatever was in hand and heat it. This did fairly well for large, smooth articles; but it was almost impossible to finish the edges of spoons so as not to show the two metals. If you look at a plated spoon to-day, however, you will find that there is no break at the edge, and so far as you can tell by the eye, it is solid silver. If you look on the back of the spoon, you will perhaps see "Rogers Bros. 1846." These men were the first silvermakers in this country to plate tableware by electricity. To make a spoon, they formed one out of iron or copper and made sure that it was perfectly clean. Then across a bath of silver cyanide, potassium cyanide, and water they[Pg 55] laid two metal rods, and from these they hung a spoon at one end and a plate of silver at the other. These rods were connected with the two poles of a battery. The electrical current passed through them, released the silver from the silver cyanide, and this was deposited upon the spoon. The cyanide that had lost its silver took enough more from the silver plate to make up. The amount of silver on the spoon depends upon the length of time it remains in the bath. It is weighed before plating and again afterwards, to make sure that the proper amount of silver has been deposited upon it. On the back of many plated articles you will see the words "Triple plate" or "Quadruple plate." If the article has been made by a reliable firm, this means that the triple plate it manufactures contains three times as much silver as "single plate," and that quadruple plate contains four times as much. A piece of silver looks just as well if it has stayed in the bath only a few minutes, but of course it has taken on so little silver that this will soon wear off and show the cheaper metal.
A large amount of silver is used for coins. When the United States needs dollars, half-dollars, quarters, and dimes, notice is given and offers are called for, stating the quantity for sale and its price. When it is delivered, it is first of all "assayed"; that is, tested to find out how nearly pure it is and how much it is worth. Next it is refined, or purified from other metals, mixed with a little copper to harden it, then melted again and poured into moulds to make bars.[Pg 56] If dollars are to be made, the bar is made thinner by passing it between heavy rollers, and blanks for dollars are cut out with a die. These blanks are weighed and every one that is too heavy or too light is put back to be melted over again. Thus far these dollars are only round, smooth pieces of metal. They must be milled to give them a rough edge, and they must be stamped. For stamping, the piece of metal is placed between two dies, one above and one below, and these close upon it with a force of one hundred and fifty tons. Every part of the process of manufacturing money is carried on with the utmost care. The places where coins are made are called "mints." The United States has four; the oldest is in Philadelphia, and there are branch mints in San Francisco, New Orleans, and Denver. Coins minted in Philadelphia have no distinguishing mark; but coins minted in San Francisco are marked with a tiny "S"; if minted in New Orleans, with an "O"; and if in Denver, with a "D."
Did you ever realize that your food and clothes, your books, and the house in which you live all depend upon iron? Vegetables, grains, and fruits are cultivated with iron tools; fish are caught with iron hooks, and many iron articles are used in the care and sale of meat. Clothes are woven on iron looms, sewed with iron needles, and fastened together with buttons containing iron. Books are printed and bound by iron machines, and sometimes written with iron pens or on iron typewriters. Houses are put together with nails; and indeed, there is hardly an article in use that could be made as well or as easily if iron was not plenty. If you were making a world and wanted to give the people the most useful metal possible, the gift would have to be iron; and the wisest thing you could do would be to put it everywhere, but in such forms that the people would have to use their brains to make it of service.
This is just the way with the iron in our world. Wherever you see a bank of red sand or red clay or a little brook which leaves a red mark on the ground as it flows, there is iron. Iron is in most soils, in red bricks, in garnets, in ripening apples, and even in your own blood. It forms one twentieth part of the[Pg 58] crust of the earth. Iron dissolves in water if you give it time enough. If you leave a steel tool out of doors on a wet night, it will rust; that is, some of the iron will unite with the oxygen of the water. This is rather inconvenient, and yet in another way this dissolving is a great benefit. Through the millions of years that are past, the oxygen of the rain has dissolved the iron in the hills and has worked it down, so that now it is in great beds of ore or in rich "pockets" that are often of generous size. One of them, which is now being mined in Minnesota, is more than two miles long, half a mile wide, and of great thickness. The rains are still at work washing down iron from the hills. They carry the tiny particles along as easily as possible until they come upon limestone. Then, almost as if it was frightened, the brook drops its iron and runs away as fast as it can. Sometimes it flows into a pond or bog in which are certain minute plants or animals that act as limestone does, and the particles of iron fall to the bottom of the pond. In colonial days much of the iron worked in America was taken from these deposits. One kind of iron is of special interest because it comes directly from the sky, and falls in the shape of stones called "meteorites," some of which weigh many tons. In some of the old fables about wonderful heroes, the stories sometimes declare that the swords with which they accomplished their deeds of prowess fell straight from the heavens, which probably means that they were made of meteoric iron. Fortunately for the people and their homes, meteorites[Pg 59] are not common, but every large museum has specimens of them.
It is not especially difficult to make iron if you have the ore, a charcoal fire in a little oven of stones, and a pair of bellows. Put on layers of charcoal alternating with layers of ore, blow the bellows, and by and by you will have a lump of iron. It is not really melted, but it can be pounded and worked. This is called the "Catalan method," because the people of Catalonia in Spain made iron in this way. It is still used by the natives of the interior of Africa. But if all the iron was made by this method, it would be far more costly than gold. The man who makes iron in these days must have an immense "blast furnace," perhaps one hundred feet high, a real "pillar of fire." Into this furnace are dropped masses of ore, and with it coke to make it hotter and limestone to carry off the silica slag, or worthless part. To increase the heat, blasts of hot air are blown into the bottom of the furnace. This air is heated by passing it through great steel cylinders as high as the furnace. The fuel used is nothing more than the gases which come out at the top of the furnace.
The slag is so much lighter than iron that when the ore is melted the slag floats on top just as oil floats on water, and can be drained out of the furnace through a higher opening than that through which the iron flows. The slag tap is open most of the time, but the iron tap is opened only once in about six hours. It is a magnificent sight when a furnace is "tapped" and the stream of iron drawn off.[Pg 60] Imagine a great shed, dark and gloomy, with many workmen hurrying about to make ready for what is to come. The floor is of sand and slopes down from the furnace. Through the center of this floor runs a long ditch straight from the furnace to the end of the shed. Opening from it on both sides are many smaller ditches; and connecting with these are little gravelike depressions two or three feet long and as close together as can be. These are called "pigs." When the time has come, the workmen gather about the furnace, and with a long bar they drill into the hard-baked clay of the tapping hole. Suddenly it breaks, and with a rush and a roar the crimson flood of molten iron gushes out. It flows down the trench into the ditches, then into the pigs, till their whole pattern is marked out in glowing iron. Now the blast begins to drive great beautiful sparks through the tapping hole. This means that the molten iron is exhausted. The blast is turned off, and the "mud-gun" is brought into position and shoots balls of clay into the tapping hole to close it for another melting, or "drive." The crimson pigs become rose-red, darken, and turn gray. The men play streams of water over them and the building is filled with vapor. As soon as the pigs are cool enough, they are carted away and piled up outside the building.
In some iron works moulds of pressed steel carried on an endless chain are used instead of sand floors. The chain carries them past the mouth of a trough full of melted iron. They are filled, borne under water to be cooled, and then dropped upon cars. A first-class machine can make twenty pigs a minute.
 IN THE STEEL FOUNDRY
IN THE STEEL FOUNDRY
It is a dangerous business to visit a steel mill. Tremendous kettles
travel overhead on huge cranes, hot metal flows from unexpected places,
and there is a constant glow and steam and roar everywhere to confuse
the unwary.
Most of the iron made in blast furnaces is turned into steel. Steel has been made for centuries, but until a few years ago the process was slow and costly. A workman's steel tools were treasures, and a good jackknife was a valuable article. Railroads were using iron rails. They soon wore out, but at the suggestion to use steel, the presidents of the roads would have exclaimed, "Steel, indeed! We might as well use silver!" Trains needed to be longer and heavier, but iron rails and bridges could not stand the strain. Land in cities was becoming more valuable; higher buildings were needed, but stone was too expensive. Everywhere there was a call for a metal that should be strong and cheap. Iron was plentiful, but steel was dear. A cheaper method of making iron into steel was needed; and whenever there is pressing need of an invention, it is almost sure to come. Before long, what is known as the "Bessemer process" was invented. One great difficulty in the manufacture of steel was to leave just the right amount of carbon in the iron. Bessemer simply took it all out, and then put back exactly what was needed. Molten iron, tons and tons of it, is run into an immense pear-shaped vessel called a "converter." Fierce blasts of air are forced in from below. These unite with the carbon and destroy it. There is a roar, a clatter, and a clang. Terrible flames of glowing red shoot up. Suddenly they change from red to yellow, then to white; and[Pg 63] this is the signal that the carbon has been burned out. The enormously heavy converter is so perfectly poised that a child can move it. The workmen now tilt it and drop in whatever carbon is needed. The molten steel is poured into square moulds, forming masses called "blooms," and is carried away. More iron is put into the converter, and the work begins again.
The Bessemer process makes enormous masses of steel and makes it very cheaply; but it has one fault—it is too quick. The converter roars away for a few minutes, till the carbon and other impurities are burned out; and the men have no control over the operation. In what is called the "open-hearth" process, pig iron, scrap iron, and ore are melted together with whatever other substances may be needed to make the particular kind of steel desired. This process takes much longer than the Bessemer, but it can be controlled. Open-hearth steel is more homogeneous,—that is, more nearly alike all the way through,—and is better for some purposes, while for others the Bessemer is preferred.
Steel is hard and strong, but it has two faults. A steel bar will stand a very heavy blow and not break, but if it is struck gently many thousand times, it sometimes crystallizes and may snap. A steel rail may carry a train for years and then may crystallize and break and cause a wreck. Inventors are at work discovering alloys to prevent this crystallization. The second fault of steel is that it rusts and loses its strength. That is why an iron bridge or[Pg 64] fence must be kept painted to protect it from the moisture in the air.
If all the iron that is in use should suddenly disappear, did you ever think what would happen? Houses, churches, skyscrapers, and bridges would fall to the ground. Railroad trains, automobiles, and carriages would become heaps of rubbish. Ships would fall apart and become only scattered planks floating on the surface of the water. Clocks and watches would become empty cases. There would be no machines for manufacturing or for agriculture, not even a spade to dig a garden. Everybody would be out of work. If you wish to see how it would seem, try for an hour to use nothing that is of iron or has been made by using iron.
Where did rocks come from?
Some were deposited in water, like limestone and like the shale and sandstone that lie over the strata of coal. Others were made by fire, and were thrown up in a melted state from the interior of the earth. Such rocks are the Giant's Causeway in Ireland and the Palisades of the Hudson River. They are called "igneous" rocks, from the Latin word ignis meaning "fire."
When the igneous rocks were thrown up to the surface of the earth, they brought various metals with them. How the metals happened to be there ready to be brought up, no one knows. Some people think they were dissolved in water and then deposited; others think that electricity had something to do with their formation. However that may be, metals were brought up with the igneous rocks, and one of these metals is copper.
Now, to one who did not know how to work iron, copper was indeed a wonderful treasure, for it made very good knives and spoons. The people who lived in this country long before the Indians came understood how to use it, and after a while the Indians themselves found out its value. They did not trouble themselves to dig for it; they simply picked it up from the ground, good pure metal in[Pg 66] lumps; and with stones for hammers they beat it into knives.
There was only one place in what is now the United States where they could do this, and that was in northern Michigan. A long point of land stretches out into Lake Superior as if it was trying to see what could be found there. Just beyond its reach is Isle Royal; and in these two places there was plenty of copper, enough for the Indians, enough for the people who have come after them, and enough for a great many more. One piece of copper which the Indians did not pick up, and the United States Government did, is the famous Ontonagon Boulder, so called because it was found near the Ontonagon River. It weighs more than three tons. The Indians would have been glad to make use of it, but it was too hard for their tools, and so they are said to have worshiped it as a god. It is now in the National Museum in Washington.
The lumps of copper, such as those which delighted the hearts of the Indians, are known to-day as "barrel" copper, because they are of a good size to be dropped into barrels and carried away for smelting. The great boulders which the Indians could not use are called "mass" copper. Sometimes they weigh as much as five hundred tons. The copper in them is almost pure, and a big boulder is worth perhaps $200,000. Nevertheless, the mine-owners do not rejoice when they come upon such a mass in their digging, for it cannot be either dug or blasted, and has to be cut away with chisels of chilled steel. Now, a mine may be wonderfully rich in metal, but if working it costs too much, then another mine with less metal but more easily worked will pay better. So it is with these great masses of copper. They are interesting to study and they look well in museums, but they do not pay so well as the "stamp" copper which is found in humble little bits in the gangue, or the rock of the vein, and has to be pounded in a stamp mill. This gangue is dug out and broken up as in mines of other metals. The copper is much heavier than the rock, so it is easy to get rid of the worthless gangue by means of a flow of water. The gangue of the Michigan mines is exceedingly hard, but the stamps are so powerful that one can crush five hundred tons in less than twenty-four hours. Some copper can be taken out of the mortars at once, but the rest of the broken gangue is fed to jigs, or screens, which are kept under jets of water. The water is thrown up from below and the lighter rock is tossed away, while the heavier copper falls through the tiny holes in the screens.
 IN A COPPER SMELTER
IN A COPPER SMELTER
The men are pouring hot copper into moulds for castings.
After the ore has been through all these experiences, it comes out looking like dark-colored sand or coarse brown sugar. It is not interesting, and no one who saw it for the first time would ever fancy that it was going to turn into something beautiful. It is dumped into freight cars and trundled off to the smelting furnaces. But however uninteresting it looks, it is well worth while to follow these cars to see what happens to it at the smelters. First of all,[Pg 69] even before it goes into the smelting furnace, it must be roasted. There is usually sulphur combined with the copper, and roasting will get rid of much of it. In some places this is done by building up a great heap of ore with a little wood. The wood is kindled, and by the time it has burned out, the sulphur in the ore has begun to burn, and in a good-sized heap it will continue to burn for perhaps two months.
Such a heap is a good thing to keep away from, for the fumes of sulphur are very disagreeable. Indeed, they will kill trees and other growing things wherever the wind may carry them, even several miles away. The managers of mines of copper as well as of gold and silver have learned to economize; and it has been found that instead of letting these fumes go into the air, they may be made to pass through acid chambers lined with zinc and full of water. The water holds the fumes, and can be used in making sulphuric acid.
After the ore has been roasted, it is put into the furnace for smelting. If you should make an oven and put into it a mixture of wood and roasted copper, that would be a smelting furnace. Set the wood on fire, pump in air to make the flame hot, and if your furnace could be made hot enough,—that is, 2300° F., or about eleven times as hot as boiling water,—you could smelt copper. Of course the furnace of a real smelting factory will hold tons and tons of copper ore and has all sorts of improvements, but after all it is in principle only an oven with wood and ore and draft. Another sort of furnace, which is[Pg 70] better for some kinds of ore, has a grate for the fire and a bed above it for the copper.
Imagine an enormous furnace holding between two and three hundred tons of metal and burning with such a terrific heat that by contrast boiling water would seem cool and comfortable. Suddenly, while you stand looking at it, but a long way off, a door flies open and the most beautiful cascade—only it is not a waterfall, but a copper fall—pours out. It looks like red, red gold, rich and wonderful, with little flames of red and blue dancing over it. It might almost be one of the fire-breathing dragons of the old story-books; and if it should get loose, it would devour whomever it touched far quicker than any dragon. It hardly seems as if any one could manage such a monster; but it looks easy, after you have seen it done. An enormous horizontal wheel revolves slowly. On its edge are moulds shaped like bricks, but much larger. On the hub of the wheel a workman sits to direct the filling of these. A set of them is filled, and moves on, and others take their place. When they are partly cooled, another workman, at the farther side of the wheel, pries them out of the mould and drops them into water. Then by the aid of the fingers of a machine and those of men, they are loaded upon cars.
In copper there is often some gold and silver. The precious metals do not make the copper any better, and if they can be separated from it, they are well worth the trouble. This is done by electricity. It is so successful that the metallurgists are hoping soon[Pg 71] to take a long step ahead and by means of electricity to produce refined copper directly from the ore. Indeed, this has been done already in the laboratories, but before the managers of mines can employ the method, a way of making it less expensive must be discovered.
No mine that wastes anything is as well managed as it might be; and superintendents are constantly on the watch for cheaper methods and for ways to make the refuse matter of use. Even the scoria, or slag from the furnaces, has been found to be good for something, and now it is made into a coarse sort of brick that for certain rough uses is of value. By the way, the shaft of a copper mine, the Red Jacket, has shown itself of use in a manner that no one expected, namely, it helps to prove that the earth turns around. This shaft is the deepest mining shaft in the world, and when you get into the cage, you go down a full mile toward the center of the earth. If you drop any article into the shaft, it always strikes the east side before reaching the bottom. The only way to explain this is that the earth turns toward the east.
Copper mixed with zinc forms brass, which is harder than copper alone. It tarnishes, though not so easily as copper; but a coat of varnish will protect it till the varnish wears off. A good way to find out the many uses of brass and to see how valuable they are is to go along the street and through a house and make a list. On the street you will see signs, harness buckles, and buttons, everywhere.[Pg 72] Look on the automobiles and fire engines for a fine display of brass, polished and shining. In the house you will find brass bedsteads, curtain rods, faucets, pipes, drawerpulls, candlesticks, gas and electric fixtures, lamps, the works of clocks and watches, and scores of other things. You will not have any idea how many they are till you begin to count.
Copper mixed with tin forms bronze. Go into a hardware store and look at the samples of bronze outside of each drawer, and you will be surprised that there are so many. Bronze does not change even when in the open air for ages. That is one reason why it has always been so much used for statues. There are two strange facts about this mixture. One is that bronze is harder than either copper or tin. The other is that if you mix one pint of melted copper with one pint of tin, the mixture will be less than a quart. Just why these things are so, no one is quite certain. Mathematics declares that the whole is equal to the sum of its parts; but in this one case the whole seems to be less than the sum of its parts.
Another reason why bronze is so much used for statues is that the castings are smooth. I once went to a foundry to have a brass ornament shaped somewhat like a cone made for a clock. The foundryman formed a mould in clay and poured the melted brass into it. When it had cooled, the mould was broken off and the ornament taken out; but it was of no use because it was so full of little hollows that it could not be made smooth without cutting away a great[Pg 73] deal of it. The man had to try three times before he succeeded in making one that could be polished. If it had been made of bronze, there would have been no trouble, because bronze, hard as it is after it cools, flows when it is melted almost as easily as molasses and fills every little nook and corner of the mould.
A famous Latin poet named Horace, who lived two thousand years ago, wrote of his poems, "I have reared a monument more lasting than bronze"; and he was right, for few statues have endured from his day to ours, but his poems are still read and admired.
Bells are made of bronze, about three quarters copper and one quarter tin. It is thought that much copper gives a deep, full tone, and that much tin with, sometimes, zinc makes the tone sharp. The age of a bell has something to do with its sound being rich and mellow; but the bellmaker has even more, for he must understand not only how to cast it, but also how to tune it. If you tap a large bell, it will, if properly tuned, sound a clear note. Tap it just on the curve of the top, and it will give a note exactly one octave above the first. If the note of the bell is too low, it can be made higher by cutting away a little from the inner rim. If it is too high, it can be made lower by filing on the inside a little above the rim. Many of the old bells contain the gifts of silver and gold which were thrown in by people who watched their founding. The most famous bell in the United States is the "Liberty Bell" of Independence[Pg 74] Hall, in Philadelphia, which rang when Independence was adopted by Congress. This was founded in England long before the Revolution and later was melted and founded again in the United States.
It would not be easy to get on without brass and bronze; but even these alloys are not so necessary as copper by itself. It is so strong that it is used in boiler tubes of locomotives, as roofing for buildings and railroad coaches, in the great pans and vats of the sugar factories and refineries. A copper ore called "malachite," which shows many shades of green, beautifully blended and mingled, is used for the tops of tables. Wooden ships are often "copper-bottomed"; that is, sheets of copper are nailed to that part of the hull which is under water in order to prevent barnacles from making their homes on it, and so lessening the speed of the vessel.
People often say that the latter half of the nineteenth century was the Age of Steel, because so many new uses for steel were found at that time. The twentieth century promises to be the Age of Electricity, and electricity must have copper. Formerly iron was used for telegraph wires; but it needs much more electricity to carry power or light or heat or a telegraphic message over an iron wire than one of copper. Moreover, iron will rust and will not stretch in storms like copper, and so needs renewing much oftener. Electric lighting and the telephone are everywhere, even on the summits of mountains and in mines a mile below the earth's surface. Electric[Pg 75] power, if a waterfall furnishes the electricity, is the cheapest power known. The common blue vitriol is one form of copper, and to this we owe many of our electric conveniences. It is used in all wet batteries, and so it rings our doorbells for us. It also sprays our apple and peach trees, and is a very valuable article. Indeed, copper in all its forms, pure and alloyed, is one of our best and most helpful friends.
Not many years ago a college boy read about an interesting metal called "aluminum." It was as strong as iron, but weighed only one third as much, and moisture would not make it rust. It was made of a substance called "alumina," and a French chemist had declared that the clay banks were full of it; and yet it cost as much as silver. It had been used in France for jewelry and knicknacks, and a rattle of it had been presented to the baby son of the Emperor of France as a great rarity.
The college boy thought by day and dreamed by night of the metal that was everywhere, but that might as well be nowhere, so far as getting at it was concerned. At the age of twenty-one, the young man graduated, but even his new diploma could not keep his mind away from aluminum. He borrowed the college laboratory and set to work. For seven or eight months he tried mixing the metal with various substances to see if it would not dissolve. At length he tried a stone from Greenland called "cryolite," which had already been used for making a kind of porcelain. The name of this stone comes from two Greek words meaning "ice stone," and it is so called because it melts so easily. The young student melted it and found that it would dissolve alumina. Then he ran an electric current through[Pg 77] the melted mass, and there was a deposit of aluminum. This young man, just out of college, had discovered a process that resulted in reducing the cost of aluminum from twelve dollars a pound to eighteen cents. Meanwhile a Frenchman of the same age had been working away by himself, and made the same discovery only two months later.
Aluminum is now made from a mineral called "bauxite," found chiefly in Georgia, Alabama, and Arkansas. Mining it is much more agreeable than coal mining, for the work is done aboveground. The bauxite is in beds or strata which often cover the hills like a blanket. First of all, the mine is "stripped,"—that is, the soil which covers the ore is removed,—and then the mining is done in great steps eight or ten feet high, if a hill is to be worked. There is some variety in mining bauxite, for it occurs in three forms. First, it may be a rock, which has to be blasted in order to loosen it. Second, it may be in the form of gray or red clay. Third, it occurs in round masses, sometimes no larger than peas, and sometimes an inch in diameter. In this form it can easily be loosened with a pickaxe, and shoveled into cars to be carried to the mill. Bauxite is a rather mischievous mineral and sometimes acts as if it delighted in playing tricks upon managers of mines. The ore may not change in the least in its appearance, and yet it may suddenly have become much richer or much poorer. Therefore the superintendent has to give his ore a chemical test every little while to make sure that all things are going on well.[Pg 78]
This bauxite is purified, and the result is a fine white powder, which is pure alumina, and consists of the metal aluminum and the gas oxygen. Cryolite is now melted by electricity. The white powder is put into it, and dissolves just as sugar dissolves in water. The electricity keeps on working, and now it separates the alumina into its two parts. The aluminum is a little heavier than the melted cryolite, and therefore it settles and may be drawn off at the bottom of the melting-pot.
There are a good many reasons why aluminum is useful. As has been said it is strong and light and does not rust in moisture. You can beat it into sheets as thin as gold leaf, and you can draw it into the finest wire. It is softer than silver, and it can be punched into almost any form. It is the most accommodating of metals. You can hammer it in the cold until it becomes as hard as soft iron. Then, if you need to have it soft again, it will become so by melting. It takes a fine polish and is not affected, as silver is, by the fumes which are thrown off by burning coal; and so keeps its color when silver would turn black. Salt water does not hurt it in the least, and few of the acids affect it. Another good quality is that it conducts electricity excellently. It is true that copper will do the same work with a smaller wire; but the aluminum is much lighter and so cheap that the larger wire of aluminum costs less than the smaller one of copper, and its use for this purpose is on the increase. It conducts heat as well as silver. If you put one spoon of aluminum, one of silver, and one that is "plated" into a cup of hot water, the handles of the first two will almost burn your fingers before the third is at all uncomfortable to touch.
 A "MOVIE" OF AN ALUMINUM FUNNEL
A "MOVIE" OF AN ALUMINUM FUNNEL
Courtesy The Aluminum Cooking Utensil Company.
Seventeen other operations are necessary after the thirteenth stamping
operation before the funnel is ready to be sold. And after all this
work, we can buy it for 35 cents at any hardware store.
Aluminum is found not only in clay and indeed in most rocks except sandstone and limestone, but also in several of the precious stones, in the yellow topaz, the blue sapphire and lapis-lazuli, and the red garnet and ruby. It might look down upon some of its metallic relatives, but it is friendly with them all, and perfectly willing to form alloys with most of them. A single ounce of it put into a ton of steel as the latter is being poured out will drive away the gases which often make little holes in castings. Mixed with copper it makes a beautiful bronze which has the yellow gleam of gold, but is hard to work. When a piece of jewelry looks like gold, but is sold at too low a price to be "real," it may be aluminum bronze, very pretty at first, but before long its luster will vanish. Aluminum bronze is not good for jewelry, but it is good for many uses, especially for bearings in machinery. Aluminum mixed with even a very little silver has the color and brightness of silver. The most common alloys with aluminum are zinc, copper, and manganese, but in such small quantities that they do not change its appearance.
With so many good qualities and so few bad ones, it is small wonder that aluminum is employed for more purposes than can be counted. A very few years ago it was only an interesting curiosity, but now it is one of the hardest-worked metals. Automobiles[Pg 81] in particular owe a great deal to its help. When they first began to be common, in 1904-05, the engines were less powerful than they are now made, and aluminum was largely employed in order to lessen the weight. Before long it was in use for carburetors, bodies, gear-boxes, fenders, hoods, and many other parts of the machine. Makers of electric apparatus use aluminum instead of brass. The frames of opera glasses and of cameras are made of it. Travelers and soldiers and campers, people to whom every extra ounce of weight counts, are glad enough to have dishes of aluminum. The accommodating metal is even used for "wallpaper," and threads of it are combined with silk to give a specially brilliant effect on the stage. It can be made into a paint which will protect iron from rust; and will make woodwork partially fireproof.
Aluminum has been gladly employed by the manufacturers of all sorts of articles, but nowhere has its welcome been more cordial than in the kitchen. Any one who has ever lifted the heavy iron kettles which were in use not so very many years ago will realize what an improvement it is to have kettles made of aluminum. But aluminum has other advantages besides its lightness. If any food containing a weak acid, like vinegar and water, is put into a copper kettle, some of the copper dissolves and goes into the food; acid does not affect aluminum except to brighten it if it has been discolored by an alkali like soda. "Tin" dishes, so called, are only iron with a coating of tin. The tin soon wears off, and[Pg 82] the iron rusts; aluminum does not rust in moisture. A strong alkali will destroy it, but no alkali in common use in the kitchen is strong enough to do more harm than to change the color, and a weak acid will restore that. Enameled ware, especially if it is white, looks dainty and attractive; but the enamel is likely to chip off, and, too, if the dish "boils dry," the food in it and the dish itself are spoiled. Aluminum never chips, and it holds the heat in such a manner as to make all parts of the dish equally hot. Food, then, is not so likely to "burn down," but if it does, only the part that sticks will taste scorched; and no matter how many times a dish "boils dry," it will never break. If you make a dent in it, you can easily pound it back into shape again. It is said that an aluminum teakettle one sixteenth of an inch in diameter can be bent almost double before it will break.
Aluminum dishes are made in two ways. Sometimes they are cast, and sometimes they are drawn on a machine. If one is to be smaller at the top, as in the case of a coffeepot, it is drawn out into a cylinder, then put on a revolving spindle. As it whirls around, a tool is held against it wherever it is to be made smaller, and very soon the coffeepot is in shape. The spout is soldered on, but even the solder is made chiefly of aluminum.
Aluminum dishes may become battered and bruised, but they need never be thrown away. There is an old story of some enchanted slippers which brought misfortune to whoever owned them.[Pg 83] The man who possessed them tried his best to get rid of the troublesome articles, but they always returned. So it is with an aluminum dish. Bend it, burn it, put acid into it, do what you will to get rid of it, but like the slippers it remains with you. Unlike them, however, it brings good fortune, because it saves time and trouble and patience and money.
A few years ago the motive power for most manufactures was steam. Electricity is rapidly taking its place; and if aluminum was good for nothing else save to act as a conductor of electricity in its various applications, there would even then be a great future before it.
Probably the first man who went to a spring for a drink and found oil floating on the water was decidedly annoyed. He did not care in the least where the oil came from or what it was good for; he was thirsty, and it had spoiled his drink, and that was enough for him. We know now that oil comes chiefly from strata of coarse sandstone, but we are not quite sure how it happened to be there. The sand which formed these strata was deposited by water ages and ages ago—we are certain of that. Another thing that we are certain of is that where the strata lie flat, there is no oil. Hot substances become smaller as they cool; and as the earth grew cooler, it became smaller. The crust of the earth wrinkled as the skin of an apple does when it dries. In the tops of these great sandstone wrinkles there is often gas; and below the gas is the place where oil is found. There is no use in looking for petroleum where the folds of the strata are very sharp, because in that case the strata crack and let the oil flow away. It is not in pools, but the porous stone holds it just as a sponge holds water. If you drop a little oil upon a stone even much less porous than sandstone, it will not be easy to wipe it off, because some of it will have sunk into the stone.
In many places the gas forces its way out, and is[Pg 85] piped to carry to houses for light and heat. Not far above Niagara Falls there was a spring of gas which flowed for years. An iron pipe was put down, and when the gas was lighted, the flame shot up three or four feet. The gas came with such force that a handkerchief put over the end of the pipe would not burn, though the flame would blaze away above it. In the country of the fire worshipers, on the shores of the Caspian Sea, fires of natural gas have been burning for ages, kindled, perhaps, by lightning centuries ago. There is a vast supply of oil in this place; and indeed there is hardly a country that has not more or less of it.
In the United States the colonists soon learned that there was petroleum in what is now the State of New York; but New York was a long way from the Atlantic seaboard in those days, and they went on contentedly burning candles or sperm whale oil, or, a little later, a rather dangerous liquid which was known as "fluid." The Indians believed that the oil which appeared in the springs was a good medicine. They threw their blankets upon the water, and when these had become saturated with the oil, they wrung them out and sold the oil. Those were the times when if a medicine only tasted and smelled bad enough, people never doubted that it would cure all their diseases, and they gladly bought the oil of the Indians.
When at last it became clear to the members of an enterprising company that oil for use in lamps could be made from petroleum, they secured some[Pg 86] land in Pennsylvania that seemed promising and set to work to dig a well. But the more they dug, the more the loose dirt fell in upon them. Fortunately for the company, the superintendent had brains, and he thought out a way to get the better of the crumbling soil. He simply drove down an iron pipe to the sandstone which contained the oil, and set his borer at work within the pipe. One morning he found that the oil had gushed in nearly to the top of the well. He had "struck oil."
This was about ten years after the rush to California for gold, and now that this cheaper and quicker method of making a well had been invented, there was almost as much of a rush to Pennsylvania for oil. With every penny that they could beg or borrow, people from the East hurried to the westward to buy or lease a piece of land in the hope of making their fortunes. A song of the day had for its refrain,—
In the course of a year or two, the first "gusher" was discovered. The workmen had drilled down some four or five hundred feet and were working away peacefully, when a furious stream of oil burst forth which hurled the tools high up into the air. Hundreds of barrels gushed out every day, and soon other gushers were discovered. The most famous one in the world is at Lakeview, California. For months it produced fifty thousand barrels of oil a day, and threw it up three hundred and fifty feet into the air in a black column, spraying the country with oil for a mile around. The oil flowed away in a river, and for a time no one could plan any way to stop it or store it. At last, however, a mammoth tank was built around the well and made firm with stones and bags of earth. This was soon full of oil; and with all this vast weight of oil pressing down upon it, the stream could not rise more than a few feet above the surface. Just why oil should come out with such force, the geologists are not quite certain; but it is thought to result from a pressure of gas upon the sandstone containing it. The flow almost always becomes less and less, and after a time the most generous well has to be pumped.
 A CALIFORNIA OIL FIELD
A CALIFORNIA OIL FIELD
For scenery, one should not go to an oil field. Looks, smell, and oil
alike are unpleasant, but every oil derrick covers a fortune and helps
to make our machinery run smoothly.
An "oil field" may extend over thousands of square miles; but within this field there are always "pools"; that is, certain smaller fields, where oil is found. When a man thinks there is oil in a certain spot, sometimes he buys the land if he is able; but oftener he gets permission of the owner to bore a well, agreeing to pay him a royalty; that is, a certain percentage of all the oil that is produced. When this has been arranged, he builds his derrick. This consists of four strong upright beams firmly held together by crossbeams. It stands directly over the place where the well is to be dug. It is from thirty to eighty feet in height, according to the depth at which it is hoped to find oil. There must also be an engine house to provide the power for[Pg 89] drilling. An iron pipe eight or ten inches in diameter is driven down through the soil until it comes to rock. Now the regular drilling begins. At the top of the derrick is a pulley. Over the pulley passes a stout rope to which the heavy drilling tools—the "string of tools," as they are called—are fastened. The drilling goes on day and night. The drill makes the hole, and the sand pump sucks out the water and loose bits of stone. When the drill has gone to the bottom of the strata which carry water, the sides of the bore are cased to keep the water out; then the drilling continues, but now the drill makes its way into the oil-bearing sandstone.
There is nothing certain about the search for oil. In some places it is near the surface, in others it is perhaps three or four thousand feet down. The well may prove to be a gusher and pour out hundreds of thousands of gallons a day; or the oil may refuse to rise to the surface and have to be pumped out even at the first. Naturally, no one is prepared for a gusher, and millions of gallons have often flowed away before any arrangements could be made for storing the oil. Sometimes a well that gives only a moderate flow can be made to yield generously by exploding a heavy charge of dynamite at the bottom, to break up the rock and, it is always hoped, to open some new oil-holding crevice that the drill has not reached.
Crude petroleum is a dark, disagreeable, bad-smelling liquid; and before it can be of much use, it must be refined. For several years it was carried in[Pg 90] barrels from the oil fields to Pittsburgh by wagon and boat, a slow, expensive process, and generally unsatisfactory to all but the teamsters. Then came the railroads. They provided iron tanks in the shape of a cylinder fastened to freight cars, much like those employed to-day. There was only one difficulty about sending oil by rail, and that was that it still had to be hauled by team to the railroad, sometimes a number of miles. At length, some one said to himself, "Why cannot we simply run a pipe directly from the well to the railroad?" This was done. Pumping engines were put in a few miles apart, and the invention was a success in the eyes of all but the teamsters. In spite of their opposition, however, pipe-lines increased.
Before this it had been necessary to build the refineries as near the oil regions as possible in order to save the expense of carrying the oil; but now they could be built wherever it was most convenient. To-day oil can be brought at a small expense from west of the Mississippi River to the Atlantic seaboard, refined, and distributed throughout that part of the country, or loaded into "tankers,"—that is, steamships containing strong tanks of steel,—and so taken across the ocean. The pipes are made of iron and are six or eight inches or more in diameter. In using them one difficulty was found which has been overcome in an ingenious fashion. Sometimes they become choked by the impurities of the oil and the flow is lessened. Then a "go-devil" is put into them. This is shaped like a cartridge, is[Pg 91] about three feet in length, composed of springs and plates of iron and so flexible that it can turn around a corner. It is so made that as it slips down the current of oil, it whirls around and in so doing its nose of sharp blades scrapes the pipes clean.
The pipes go over hills and through swamps. They cross rivers sometimes by means of bridges, and sometimes they are anchored to the bed of the stream. If they have to go through a salt marsh, they are laid in concrete to preserve the iron. If these lines were suddenly destroyed and oil had to be carried in the old way, kerosene would become an expensive luxury.
Getting the oil out of the ground and carried to the refineries is not all of the business by any means. The early oils crusted on the lamp wicks, their smell was unendurable, and they were given to exploding. Evidently, if oil was to be used for lighting, it must be improved, and the first step was to distil it. To distil anything means to boil it and collect the vapor. If you hold a piece of cold earthenware in the steam of a teakettle, water will collect on it. This is distilled water, and is purer than that in the kettle. Petroleum was at first distilled in a rough way; but now it is done with the utmost care and exactness. The crude oil is pumped into boilers holding six hundred barrels or more. The fires are started, and the oil soon begins to turn into vapor. This vapor passes through coils of pipe or long, straight, parallel pipes. Cold water is pumped over these pipes, the vapor turns into a liquid again, and we have kerosene oil.[Pg 92]
This is the outline of the process, but it is a small part of the actual work in all its details. Kerosene oil is only one of the many substances found in petroleum. Fortunately, some of these substances are light, like gasoline and benzine; some, like kerosene, are heavier; and paraffin and tar are heaviest of all. There are also gases, which pass off first and are saved to help keep the furnace going. Then come the others, one by one, according to their weight. The stillman keeps close watch, and when the color and appearance of the distillate changes, he turns it off into another tank. This process is called "fractional distillation," and the various products are called "fractions." No two kinds of petroleum and no two oil wells are just alike, and it needs a skillful man to manage either.
Even after all this distillation, the kerosene still chars the wick somewhat—which prevents the wick from drawing up the oil properly—and it still has a disagreeable smell. To fit it for burning in lamps, it must be treated with sulphuric acid, which carries away some of the impurities, and then with caustic soda, which carries away others. Before it can be put on the market, it is examined to see whether it is of the proper color. Then come three important tests. The first is to see that it is of the proper weight. If it is too heavy, it will not burn freely enough; if it is too light, then there is too much of the lighter oils in it for safety. The second test is the "flash test." The object of this is to see how hot the oil must be before it gives off a vapor[Pg 93] which will burn. The third, the "burning test," is to discover how hot the oil must be before it will take fire and burn on the surface. Most civilized countries make definite laws forbidding the sale of kerosene oil that is not up to a standard of safety. Oil for use in lamps should have an open flash test of at least 100° F. and a burning point of not less than 125° F.
We say that we burn oil in our lamps, but what we really do is to heat the oil until it gives off gas, and then we burn the gas. To keep the flame regular and help on the burning, we use a chimney on the lamp. The hot air rises in the chimney and the cold air underneath rushes in to take its place and brings oxygen to the flame. In a close, stuffy room no lamp will give a good clear light, because there is not oxygen enough for its flame. Let in fresh air, and the light will be brighter. If you hold a cold plate in the flame before the chimney is put on, soot or carbon will be deposited. A lamp gives light because these particles of carbon become so hot that they glow. In lamps using a "mantle," there is the glow not only of these particles, but also of the mantle. In a wax candle, we light the wick, its heat melts the wax and carries it to the flame. When the wax is made hot enough, it becomes gas, and we burn the gas, not the wax. Wax alone will melt, but not take fire even if a burning match is held to it. The reason is that the match does not give heat enough to turn the wax into gas. But put a bit of wax upon a bed of burning coals, where there is a good supply of heat, and it will turn into gas and burn.[Pg 94]
The products made from petroleum are as different in their character and uses as paraffin and naphtha. Some of them are used for oiling machinery; tar is used for dyes; naphtha dissolves resin to use in varnish; benzine is the great cleanser of clothes, printers' types, and almost everything else; gasoline runs automobiles, motors, and many sorts of engines; paraffin makes candles, seals jelly glasses, covers the heads of matches so that they are no longer spoiled by being wet, and makes the ever-useful "waxed paper"; printers' ink and waterproof roofing-paper both owe a debt to petroleum. Even in medicine, though a little petroleum is no longer looked upon as a cure-all, vaseline, one of its products, is of great value. It can be mixed with drugs without changing their character, and it does not become rancid. For these reasons, salves and other ointments can be mixed with it and preserved for years.
The most interesting mine in the world is that of Wieliczka in Poland. In it there are some thirty miles of streets and alleys; there are churches with pillars, shrines, and statues; there are stairs, monuments, and restaurants; there is a ballroom three hundred feet long and one hundred and ninety feet high, with beautiful chandeliers, and in it is a carven throne whereon the Emperor Franz Joseph sat when he visited the mine. There are lakes crossed by ferryboats. There is a railroad station for the mule trains which bear the precious mineral salt, for this is a salt mine, and shrines, statues, churches, chandeliers—everything—are all cut out of salt.
This mine has been worked for at least eight hundred years and still has salt enough to supply all Europe for ages. The mass of salt is believed to be five hundred miles long, fifty miles wide, and nearly a quarter of a mile thick. It is so pure that it is sold just as it comes from the mine, either in blocks or finely ground. This mine is a wonderful place to visit, almost like an enchanted palace, for as the torchlight strikes the crystals of salt, they flash and sparkle as if the wall was covered with rubies and diamonds.
There is nothing like an enchanted palace in any[Pg 96] salt mine of the United States, no statues or chapels or chandeliers. There is only a hole in the ground, where mining is carried on in much the same manner as in other kinds of mines. The shaft is sunk and lined with timbers to keep the dirt from falling in, just as in other mines. In working salt mines, however, water is almost as bad as earth, and therefore a layer of clay is put between the timbers and the earth. There are the usual galleries and pillars, with roof and floor of salt. The workmen try to get the salt out in lumps or blocks as far as possible, and so they bore in drill holes and then blast with dynamite or powder. The salt is loaded upon little cars, running on tracks, and is carried up the shaft and to the top of a breaker, usually more than one hundred feet above the surface of the ground. There it is dumped upon a screen of iron bars, which lets the fine salt fall through. The large lumps are sold without crushing or sifting, and are used for cattle and sheep.
One of the great deposits of salt is in southeastern California. It is thought that the Gulf of California used to run much farther north than it now does, and that the earth rose, shutting away part of it from the ocean. This imprisoned water was full of salt. In time it dried, and the sand blew over it till it was far underground. A better way than digging was found to work it, as will be seen later; but while digging was going on, the workmen built a cottage of blocks of salt, clear and glassy. The little rain that falls there melted the blocks only enough to[Pg 97] unite them firmly together; and there the house has stood for many years.
Countries that have no deposits of rock salt can easily get plenty of salt from the water of the ocean if they only have a seacoast. About one thirtieth of the ocean water is salt, and if the water is evaporated, the salt can be collected without difficulty. France makes a great deal of salt in this way. When a man goes into the manufacture, or rather, the collecting of salt, he first of all buys or rents a piece of land,—perhaps several acres of it,—that lies just above high water, and makes it as level as possible. Unless it is very firm land, he covers it with clay, so that the water will not soak through it. Then he divides it into large square basins, making each a little lower than the one before it. Close beside the highest basin he makes a reservoir which at high tide receives water from the ocean. This flows slowly from the reservoir through one basin after another, becoming more and more salt as the water evaporates. At length the water is gone, and the salt remains. The workmen take wooden scrapers and push the salt toward the walls of the basins and then shovel it up on the dikes and heap it into creamy cones that sparkle in the sunshine. The dikes are narrow, raised pathways beside the basins and between them. As you walk along on top of them, you can smell a faint violet perfume from the salt. Thatch is put over the cones to protect them from the rain, and there they stand till some of the impurities drain away. This salt is not perfectly white,[Pg 98] because the workmen cannot help scraping up a little of the gray or reddish clay with it. Most of it is sold as it is, nevertheless, for many people have an absurd notion that the darker it is the purer it is. For those who wish to buy white salt it is sent to a refinery to be washed with pure water, then boiled down and dried.
So it is that the sun helps to manufacture salt. In some of the colder countries, frost does the same work, but in a very different manner. When salt water freezes, the water freezes, but the salt does not, and a piece of salt water ice is almost as pure as that made of fresh water. Of course, after part of the water in a basin of salt water has been frozen out, what is left is more salt than it was at first, and after the freezing has been repeated several times, only a little water remains, and evaporation will soon carry this away, leaving only salt in the basin, waiting to be purified.
Not very many years ago one of the encyclopædias remarked that "the deposits of salt in the United States are unimportant." This was true as far as the working of them was concerned, but in 1913 the United States produced more than 34,000,000 barrels. Part of this was made by evaporation of the waters of salt springs, and a small share from Great Salt Lake in Utah. The early settlers in Utah used to gather salt from the shallow bays or lagoons where the water evaporated during the summer; but now dams of earth hold back the water in a reservoir. In the spring the pumps are put to work[Pg 99] and the reservoir is soon filled with water. This is left to stand and give the impurities a chance to settle to the bottom. Then it is allowed to flow into smaller basins, while more water is pumped into the reservoir. When autumn comes, the crop of salt is ready to be harvested. It is in the form of a crust three to six inches thick, some of it in large crystals, and some fine-grained. This crust is broken by ploughs, and the salt is heaped up into great cones and left for the rain to wash clean. Then it goes to the mill for purifying. The water of Great Salt Lake is much more salty than that of the ocean. It preserves timber remarkably well, and often salt from the lake is put around telephone poles, seventy-five pounds being dropped into the hole for each one. It has been suggested to soak timber in the Lake, and then paint it with creosote to keep the wet out and the salt in.
Salt is also made from the waters of salt springs, which the Indians thought were the homes of evil spirits. At Salton, in California, an area of more than one thousand acres, which lies two hundred and sixty-four feet below sea level, is flooded with water from salt springs. When this water has evaporated, all these acres are covered with salt ten to twenty inches thick, and as dazzlingly white as if it was snow. This great field is ploughed up with a massive four-wheeled implement called a "salt-plough." It is run by steam and needs two men to manage it. The heavy steel ploughshare breaks up the salt crust, making broad, shallow furrows and[Pg 100] throwing the salt in ridges on both sides. The plough has hardly moved on before the crust begins to form again. This broken crust is worked in water by men with hoes in order to remove the bits of earth that stick to it, then piled up into cones to drain, loaded upon flat trucks, and carried to the breaker. The salt fields are wonderfully beautiful in the moonlight, but not very agreeable to work in, for the mercury often reaches 140° F., and the air is so full of particles of salt that the workers feel an intense thirst, which the warm, brackish water does not satisfy. The work is done by Indians and Japanese, for white people cannot endure the heat.
A large portion of the salt used in the United States comes directly from rock salt strata, hundreds of feet below the surface of the ground. These were perhaps the bed of the ocean ages and ages ago. There is a great extent of the beds in New York, Michigan, Ohio, Kansas, and other States. In Michigan there is a stratum of rock salt thirty to two hundred and fifty feet thick and some fifteen hundred to two thousand feet below the surface. To mine this would be a difficult and expensive undertaking, and a far better way has been discovered. First, a pipe is forced down through the surface dirt, the limestone, and the shale to the salt stratum. The drill works inside this pipe and bores a hole for a six-inch pipe directly into the salt. A three-inch pipe is let down inside of the six-inch pipe, and water is forced down through the smaller pipe. It dissolves the salt, becomes brine, and rises[Pg 101] through the space between the two pipes. It is carried through troughs to some great tanks, and from these it flows into "grain-settlers," then into the "grainers" proper, where the grains of salt settle. At the bottom of the grainers are steam pipes, and these make the brine so hot that before long little crystals of salt are seen floating on the surface of the water. Crystals form much better if the water is perfectly smooth, and to bring this about a very little oil is poured into the grainer. It spreads over the surface in the thinnest film that can be imagined. The water evaporates, and the tiny crystals grow, one joining to another as they do in rock candy. When they become larger, they drop to the bottom of the grainer. They are now swept along in a trough to a "pocket," carried up by an endless chain of buckets, and then wheeled away to the packinghouse.
The finest salt is made by using vacuum pans. These are great cans out of which the air is pumped, and into which the brine flows. This brine, heated by steam pipes, begins to boil, and as the steam from it rises, it has to pass through a pipe at the top and is thus carried into a small tank into which cold water is flowing. The cold makes the steam condense into water, which runs off. The condensed water occupies less space than the steam and so maintains the vacuum in the pan. For a perfect vacuum the brine is boiled at less than 100° F., while in an open pan or grainer it requires 226° to boil brine. The brine is soon so rich in salt that tiny[Pg 102] crystals begin to form. These are taken out and dried. If you look at some grains of table salt through a magnifying glass, you can see that each grain is a tiny cubical crystal. Sometimes two or three are united, and often the corners are rounded off and worn, but they show plainly that they are little cubes.
Most of the salt used on our tables is made by the vacuum process or by an improved method which produces tiny flakes of salt similar to snowflakes. The salt brine is heated to a high temperature and filtered. In the filters the impurities are taken out, and this process gives us very pure salt. The tiny flakes dissolve more easily than the cubes of salt, and thus flavor food more readily.
With a few savage tribes salt is regarded as a great luxury, but with most peoples it is looked upon as a necessity. Some of the early races thought a salt spring was a special gift of the gods, and in their sacrifices they always used salt. In later times to sit "above the salt," between the great ornamental salt cellar and the master of the house, was a mark of honor. Less distinguished guests were seated "below the salt." To "eat a man's salt" and then be unfaithful to him has always been looked upon as a shameful act; and with some of the savages, so long as a stranger "ate his salt,"—that is, was a guest in the house of any one of them,—he was safe. To "eat salt together" is an expression of friendliness. Cakes of salt have been used as money in various parts of Africa and Asia. "Attic salt" means wit,[Pg 103] because the Athenians, who lived in Attica, were famous for their keen, delicate wit. To take a story or a statement "with a grain of salt" means not to accept it entirely, but only to believe it partially. When Christ told his disciples that they were "the salt of the earth," he meant that their lives and teaching would influence others just as salt affects every article of food and changes its flavor. Our word "salary" comes from the Latin word sal, meaning salt; and salarium, or "salt-money," was money given for paying one's expenses on a journey. Living without salt would be a difficult matter. Cattle that have been shut away from it for a while are almost wild to get it. Farmers living among the mountains sometimes drive their cattle to a mountain pasture to remain there through the summer, and every little while they go up to salt the animals. The cattle know the call and know that it means salt; and I have seen them come rushing down the mountain-side and through the woods, over fallen trees, through briers, and down slippery rocks, bellowing as they came, and plunging head first in a wild frenzy to get to the pieces of rock salt that were waiting for them.
35 cents net. Postpaid
An Introductory Book to Precede any Series of Arithmetics
BY
FRANKLIN S. HOYT
Formerly Assistant Superintendent of Schools, Indianapolis
AND
HARRIET E. PEET
Instructor in Methods of Teaching Arithmetic, State Normal School, Salem, Massachusetts
The work is based upon the familiar experiences and activities of children, and follows as closely as possible the child's own method of acquiring new knowledge and skill.
Thus we have lessons based on playing store, making tickets, mailing letters, fishing, etc. Every step is made interesting, but no time is wasted in mere entertainment.
By the same authors
| THREE-BOOK COURSE | |
| Book One, grades II-IV. | $.40 |
| Book Two, grades V-VI | .40 |
| Book Three, grades VII-VIII | .45 |
| TWO-BOOK COURSE | |
| Book One, grades II-IV. | $.40 |
| Book Two, grades V-VIII. | .72 |
| Course of Study (with answers) | $.25 |
Distinctive Features
1. Their socialized point of view—all problems and topics taken from the everyday life of children, home interests, community interests, common business and industries. 2. Their attractiveness to children—spirited illustrations, legible page, interesting subject matter. 3. The omission of all antiquated topics and problems. 4. The grouping of problems about a given life situation. 5. The development of accuracy and skill in essential processes. 6. The vocational studies. 7. The careful attention to method. 8. The exact grading. 9. The systematic reviews. 10. The adaptation to quick and to slow pupils.
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN COMPANY
BOSTON NEW YORK CHICAGO
1901
EDITED BY
Superintendent of Schools, Springfield, Mass.
AND
Late Director of Art, Indianapolis. Formerly Principal of the Wealthy Avenue Public School, Grand Rapids, Mich.
ASSISTED BY
Instructor in Elementary Education, College for Teachers, University of Cincinnati, Formerly Supervisor of Elementary Grades, Decatur, Ill.
ILLUSTRATED BY
RUTH MARY HALLOCK
MAGINEL WRIGHT ENRIGHT
CLARA E. ATWOOD
E. BOYD SMITH
HOWARD PYLE, and other notable artists
FRESH MATERIAL
These Readers contain an unusually large amount of fresh copyrighted material taken from the world's best literature for children.
LATEST TEACHING METHODS
They represent the latest developments in the methods of teaching reading, the kind of teaching that will be found in the best schools of to-day.
ARTISTIC MAKE-UP
Artistically the books will set a new standard in text-book making. The colored Illustrations of the primary books are particularly attractive.
MECHANICAL FEATURES
The paper used in the books, the type for each grade, and the dimensions and arrangement of the type page were all determined by careful experimenting, in order to safeguard the eyesight of children.
Send for complete illustrated circular describing the unique plan of this series.
PRICES
| Primer | 30 cents, net. |
| First Reader | 35 cents, net. |
| Second Reader | 40 cents, net. |
| Third Reader | 50 cents, net. |
| Fourth Reader | 55 cents, net. |
| Fifth Reader | 55 cents, net. |
| Sixth Reader | 55 cents, net. |
| Seventh Reader | 55 cents, net. |
| Eighth Reader, | 60 cents, net. |
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN COMPANY
BOSTON NEW YORK CHICAGO
1901
The List of Illustrations was added, and some of the illustrations have been moved from their original positions to avoid breaking up paragraphs of text.
End of Project Gutenberg's Diggers in the Earth, by Eva March Tappan
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK DIGGERS IN THE EARTH ***
***** This file should be named 24762-h.htm or 24762-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/2/4/7/6/24762/
Produced by Diane Monico and The Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive/American Libraries.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.net/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.net),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.net
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.