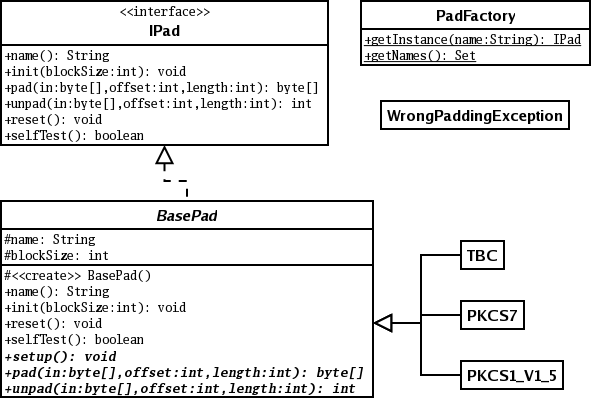
IPad interface is used seperately from ciphers and modes. The
methods defined by padding schemes are:
| void init (int bs) throws java.lang.IllegalStateException, java.lang.IllegalArgumentException | Function |
Initializes this padding scheme for the specified block size. This
method throws a java.lang.IllegalStateException if this instance
has already been initialized but not reset, and will throw a
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException if bs is not a supported
block size.
|
| void reset ( ) | Function |
| Resets this instance, which may then be re-initialized later. |
| byte [] pad (byte[] input, int offset, int length) | Function |
| Examines the bytes in input as the plaintext, starting at offset and considering length bytes, and returns the appropriate, possibly empty, byte array containing the padding. |
| int unpad (byte[] input, int offset, int length) throws WrongPaddingException | Function |
Examines the bytes in input as the plaintext, starting at
offset and considering length bytes, and returns the number
of bytes that should be trimmed off the end of input to unpad the
plaintext. Throws a WrongPaddingException if the padding bytes to
not correspond to the bytes expected by this padding scheme.
|
| java.lang.String name ( ) | Function |
| Returns the canonical name of this instance. |
| boolean selfTest ( ) | Function |
| Performs a simple conformance test on the padding scheme, to avoid implementation or run time errors. |